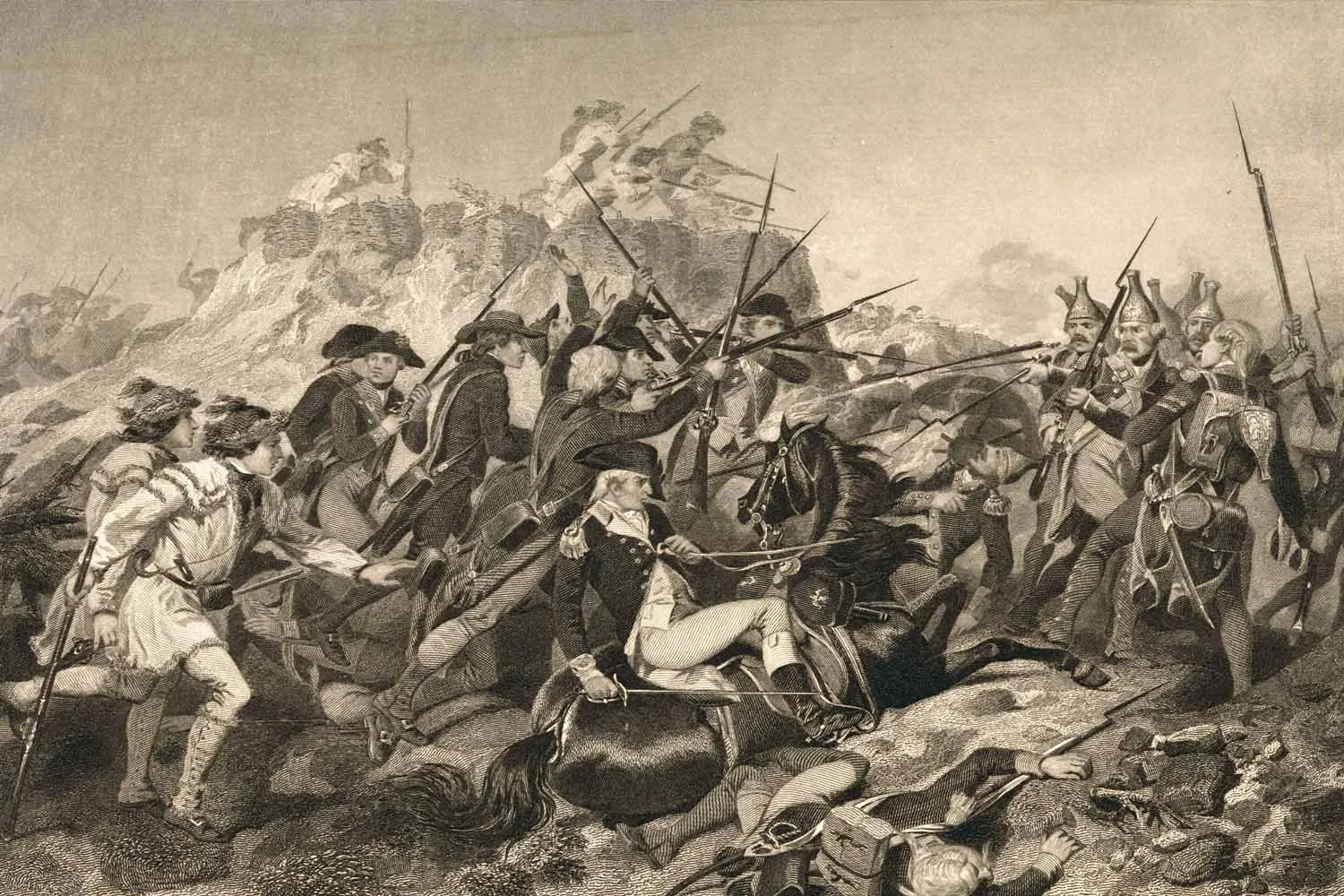


British and Americans Clash at Saratoga
By mid-September 1777, British General John Burgoyne, after crossing to the west bank of the Hudson River, was committed to continuing his advance towards Albany. There was only one road he could take to get there, and that road was strongly defended by an American army, twice as large as his own.
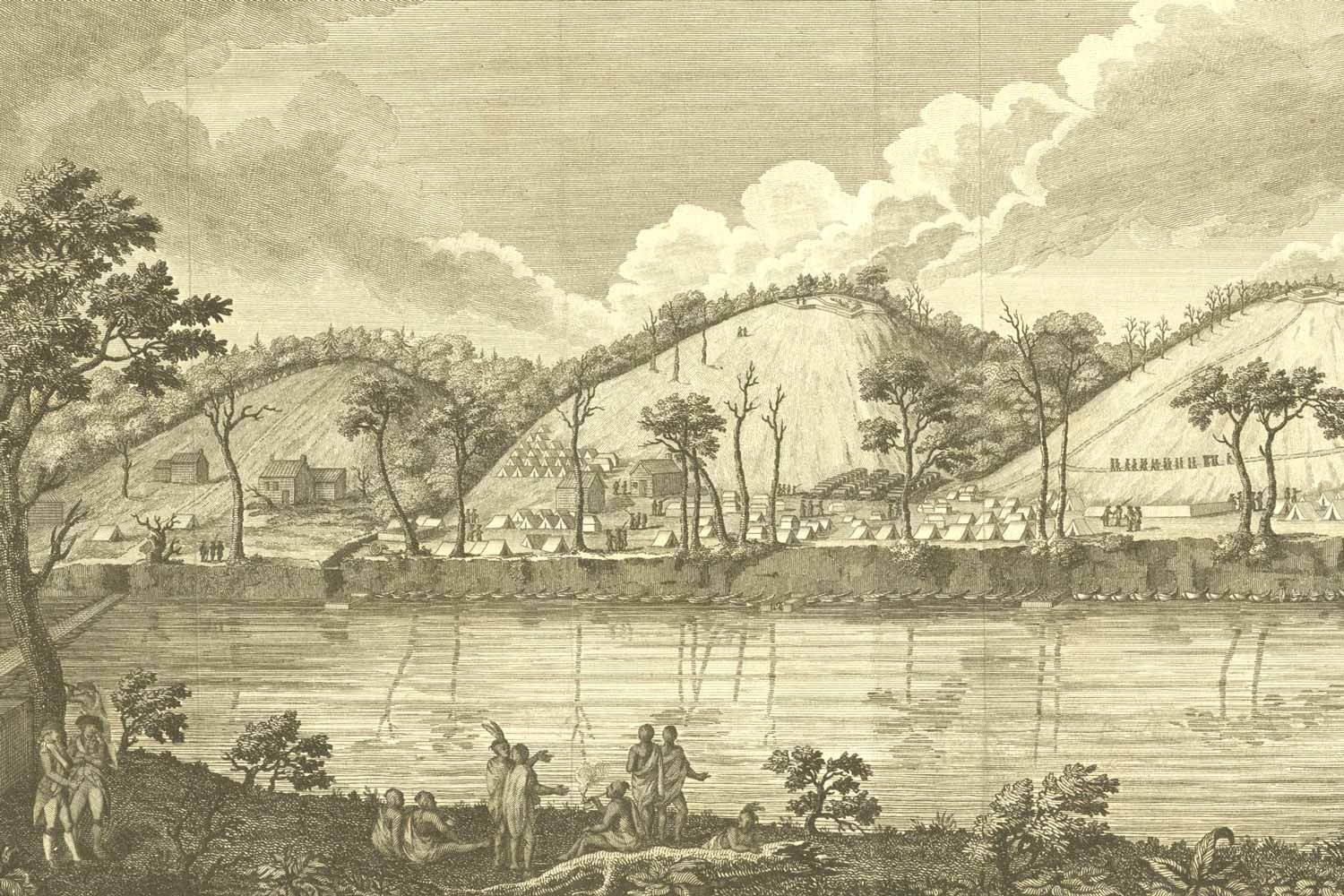

British and Americans Poised for Battle
In the eight short weeks since capturing Fort Ticonderoga without a fight, British General John Burgoyne had seen his army go from being invincible to facing starvation and defeat. More bad news arrived on August 28, when Indians brought word that a relief force under Lieutenant Colonel Barry St. Leger coming from the west down the Mohawk River Valley had turned back.
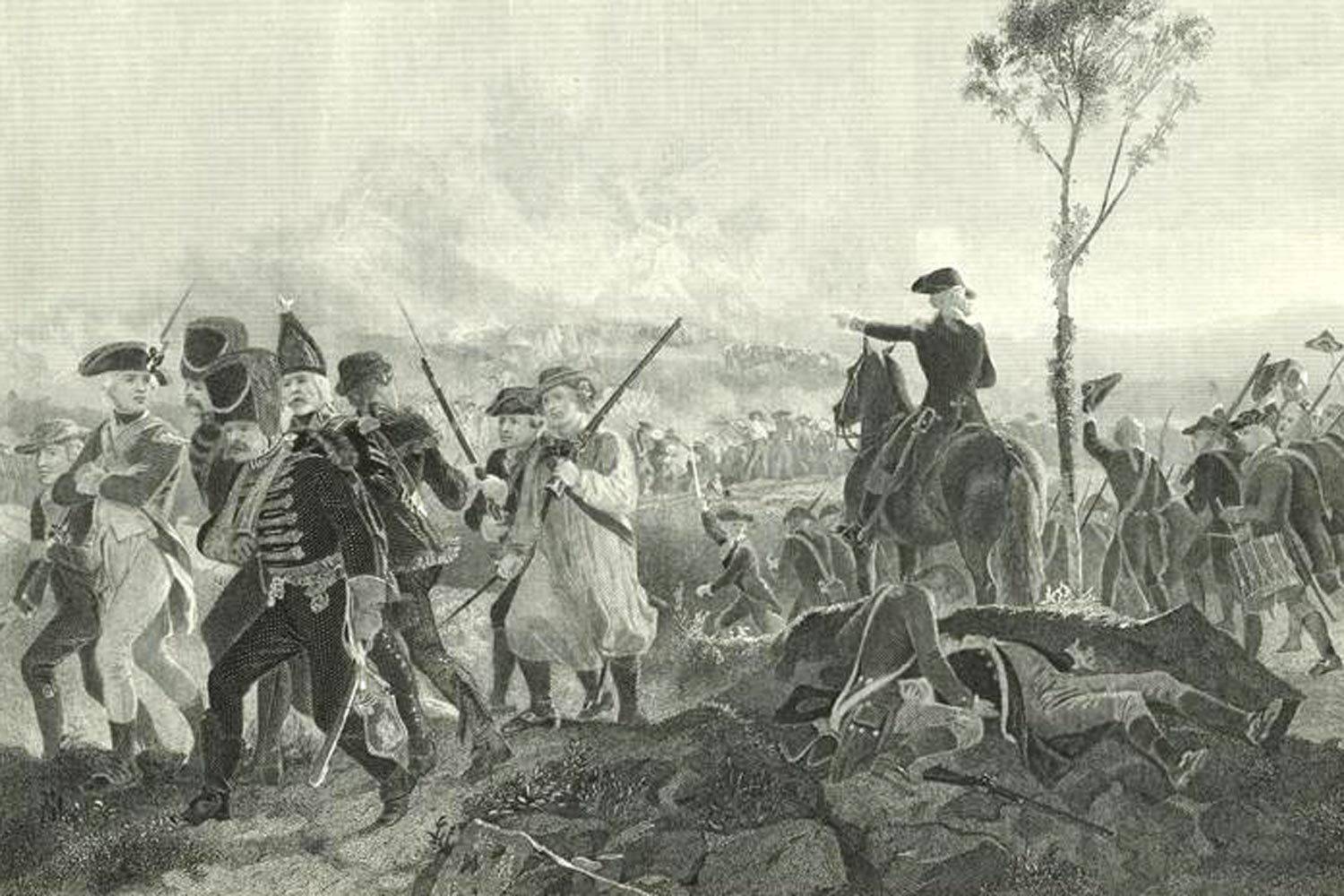

Burgoyne Battles American Wilderness and Continental Army
Despite his early successes of capturing Fort Ticonderoga and defeating the American rear guard at both Hubbardton and Fort Anne, Burgoyne now faced the greatest adversary of an army invading a foreign land: a lengthening supply line. As Napoleon remarked, an army marches on its stomach and the British soldiers were no exception.
Fort Ticonderoga Falls to British
The first objective for the British task force under the command of General John Burgoyne was the capture of Fort Ticonderoga on the south end of Lake Champlain. This fortress had been the key military site in the region since its construction in 1757, and the scene of conflicts both in the French and Indian War and the American Revolution.

British Begin the Saratoga Campaign
The Saratoga Campaign of 1777 was arguably the most significant military event during the American Revolution. If the British had achieved their goals, the American colonies would have been split in two and it is very likely that our quest for independence would have failed.
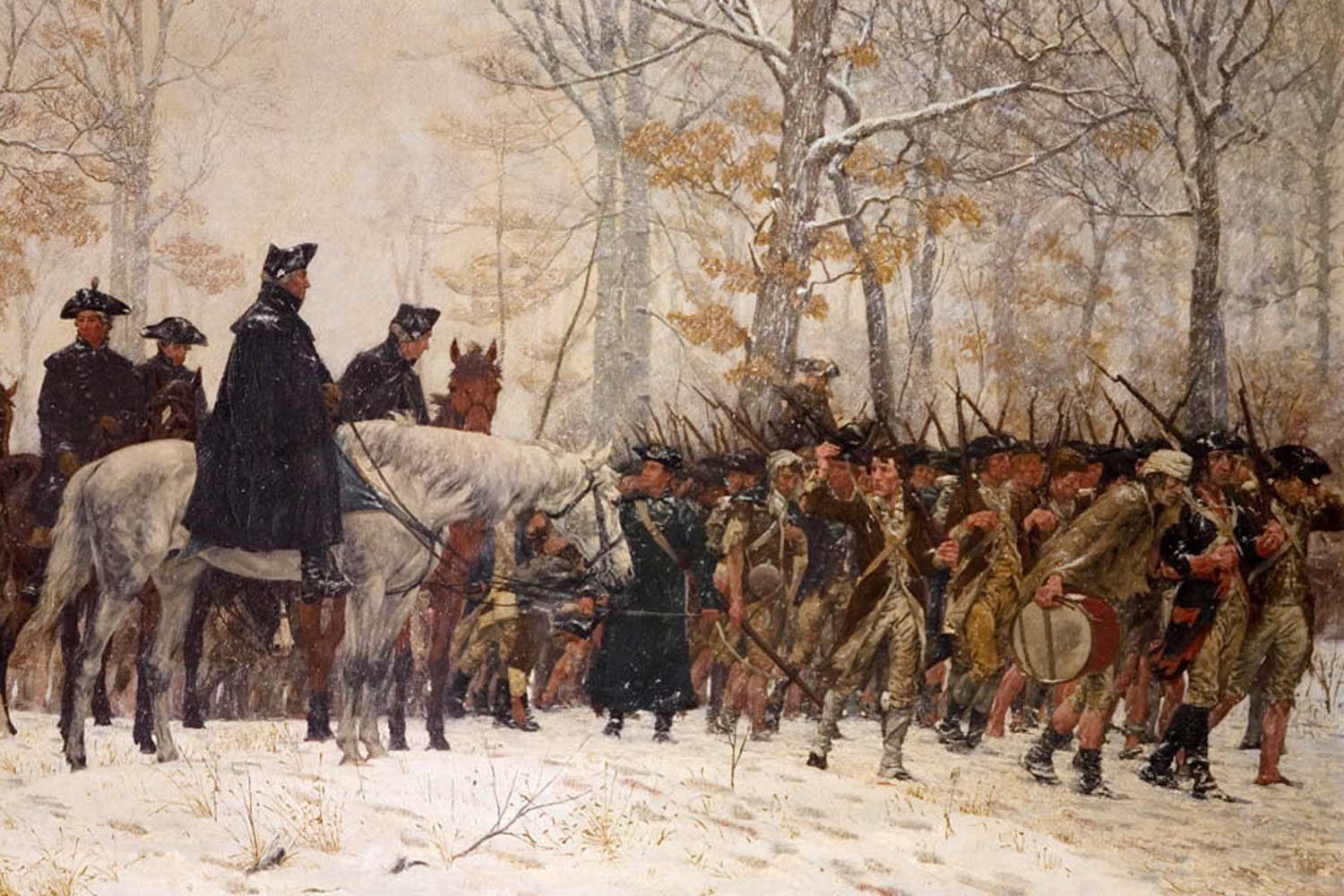

A Desperate Winter at Valley Forge
In December 1777, following the loss of Philadelphia, our nation’s capital, General George Washington moved his Continental Army to Valley Forge for the winter. It would prove to be a desperately hard winter for the soldiers, with conditions that might have broken the spirit of less determined men, but one from which the American army emerged a more professional fighting force.

The British Capture Philadelphia
Our nation’s capital has twice been captured by a foreign army and in both cases, it was by British Redcoats. The more famous incident was the burning of Washington on August 24, 1814, during the War of 1812. However, the first occurred 37 years before that event, in 1777, when the British captured Philadelphia, the capital of newly independent United States.
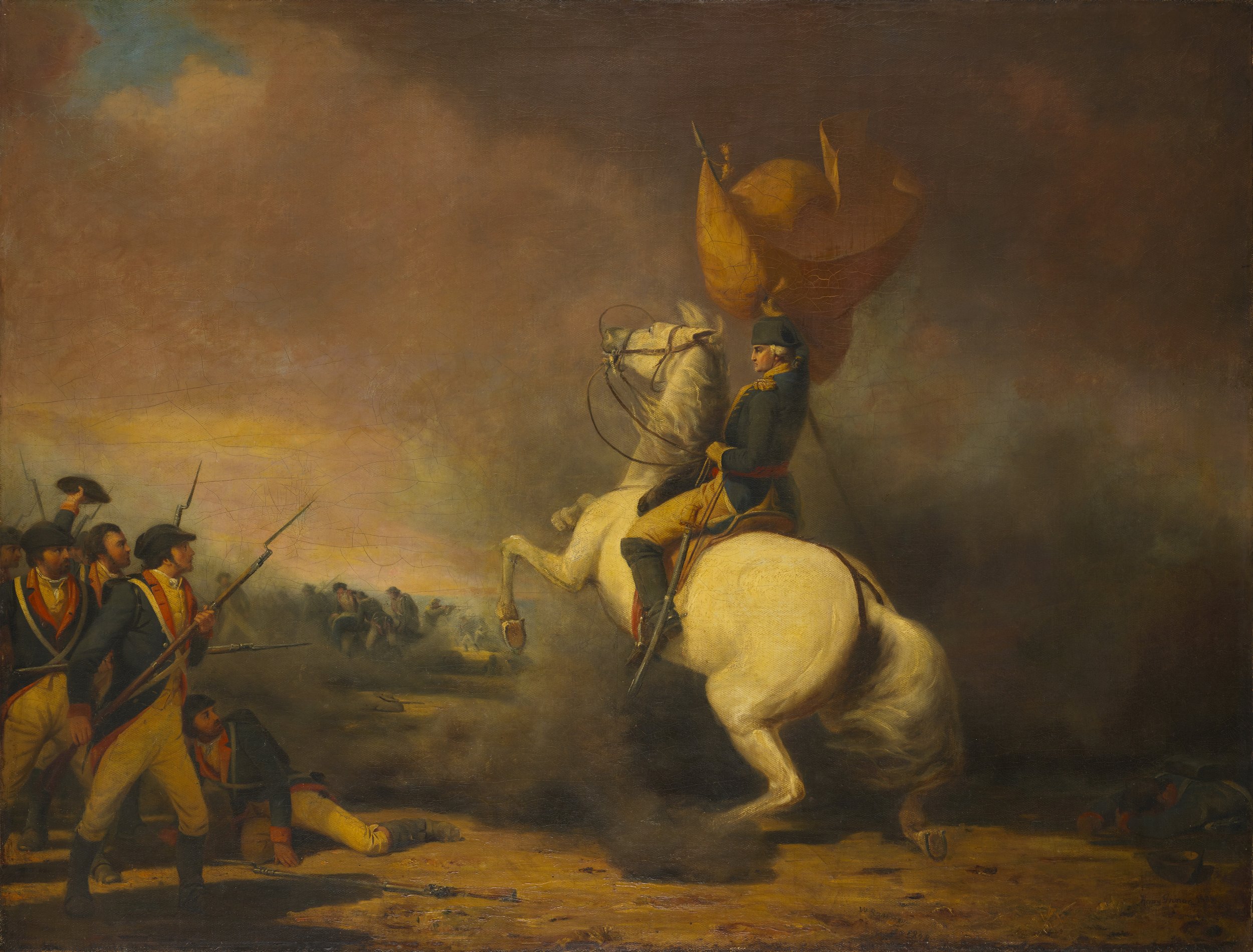

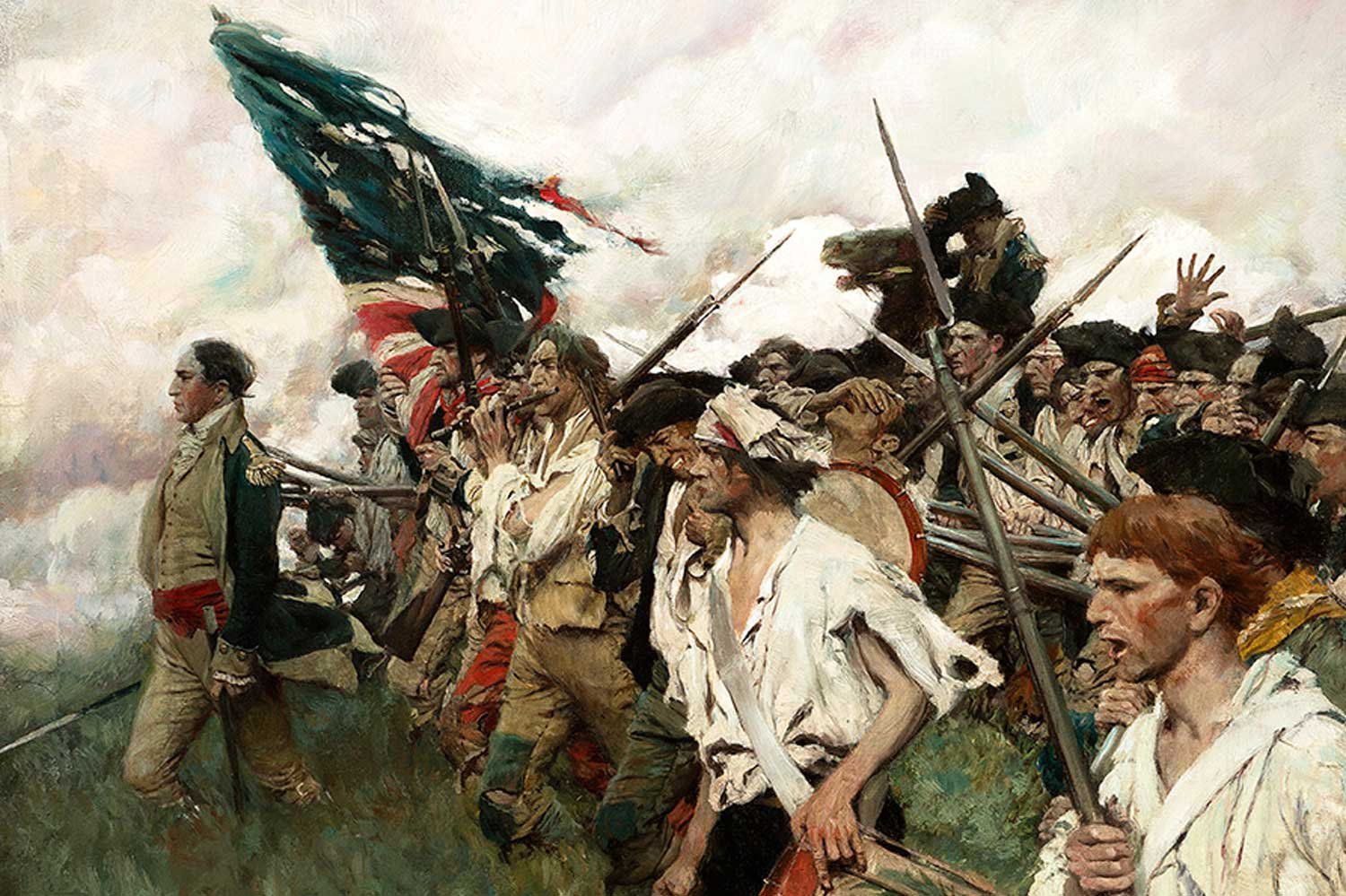
Continental Army Victorious at Princeton
General George Washington and his Continentals had achieved a great victory at Trenton on December 26, but the General saw another opportunity if he acted aggressively. On December 30, he recrossed the Delaware hoping for another miracle.
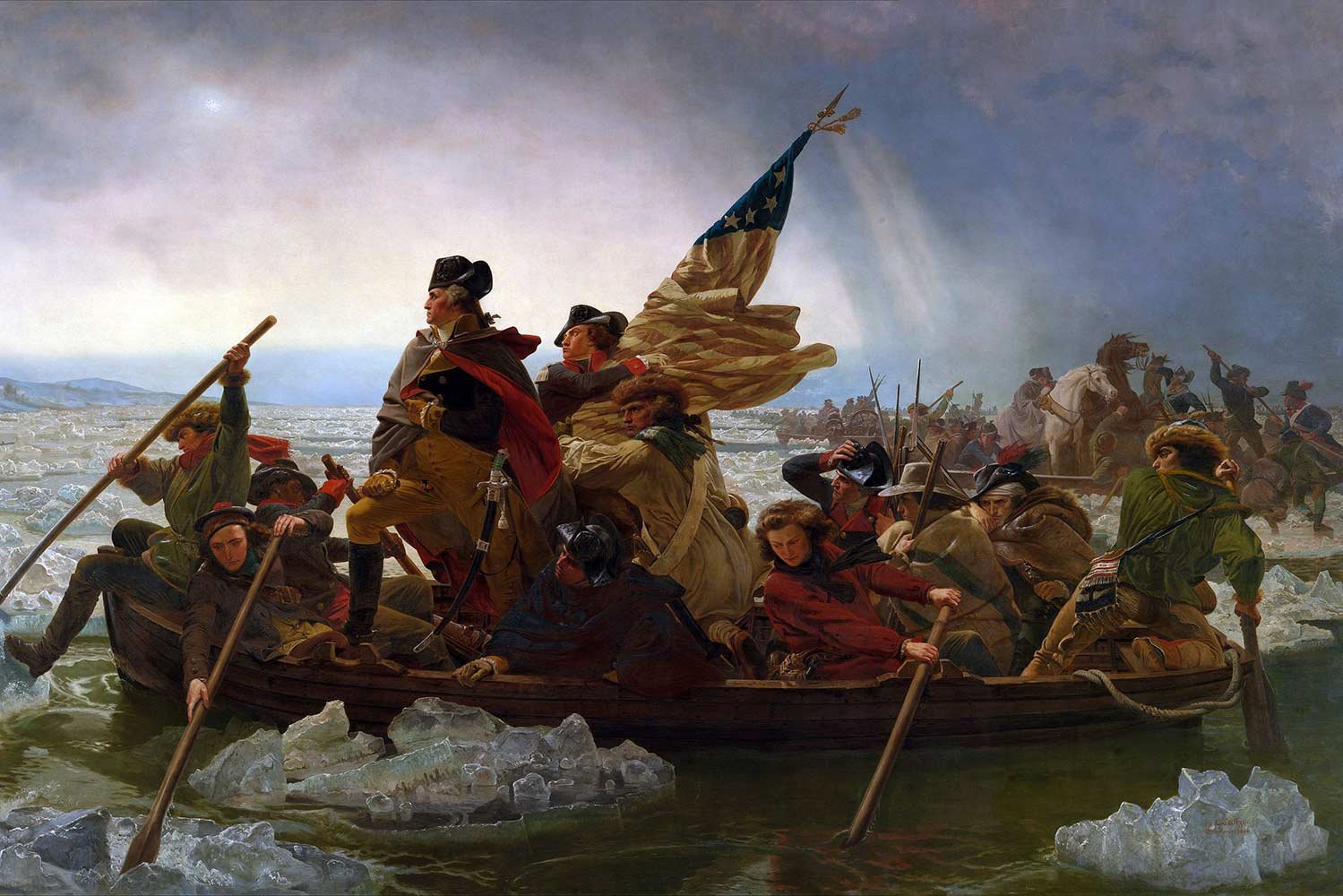

George Washington and the Crossing of the Delaware
In late December 1776, the American Revolution had reached its low point. The 16,000-man Continental Army that had driven the British out of Boston in March 1776, had lost countless battles over the course of nine months and dwindled to a skeletal force of 3,000 soldiers on the west side of the Delaware River.
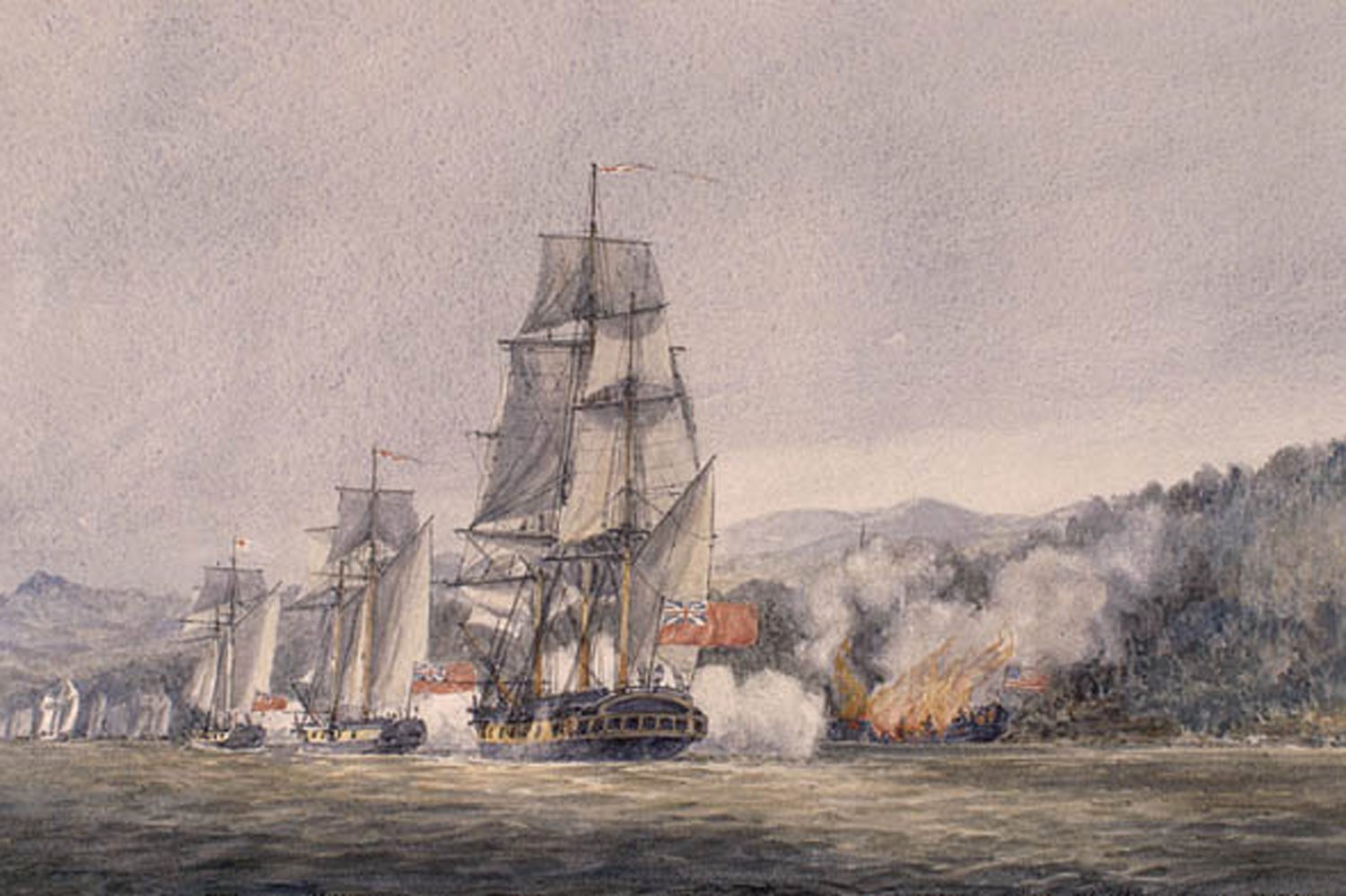
Northern Campaign Ends with Battle of Valcour Island
The Battle of Valcour Island, which took place on Lake Champlain, was the closing scene of the Northern Campaign of 1775-1776. It was one of the first naval battles of the American Revolution and, although a tactical defeat, it was a strategic victory for the American cause.
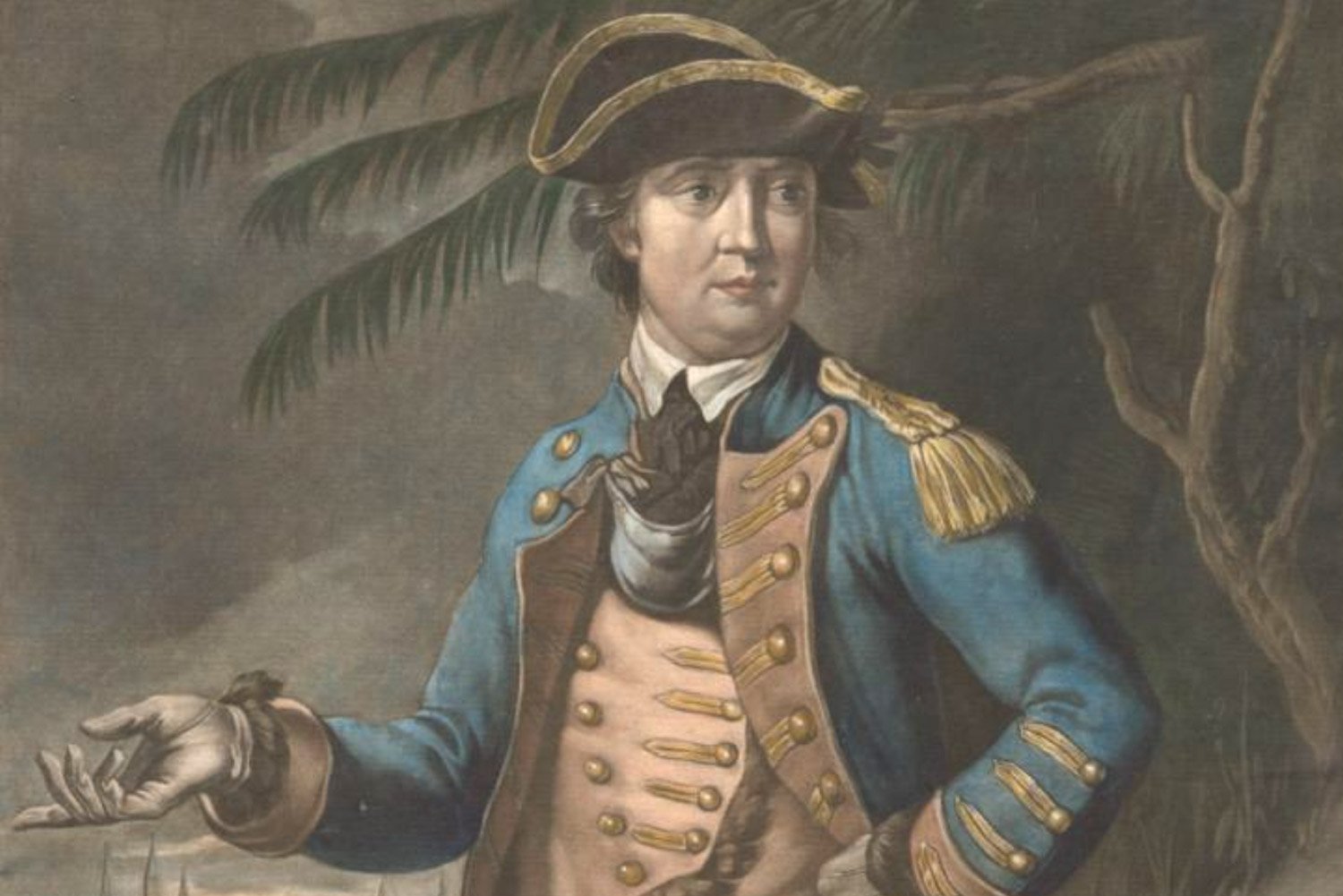

Americans Retreat After Failed Assault on Quebec
General Guy Carleton, the man in charge of British forces in Canada, chose to return to the safety of Quebec’s walls after repelling the American assault on the city instead of venturing out and attacking the remaining Americans. With the death of General Richard Montgomery, Colonel Benedict Arnold assumed command of the American army outside Quebec and, despite the setback, refused to give up on the conquest of Canada.
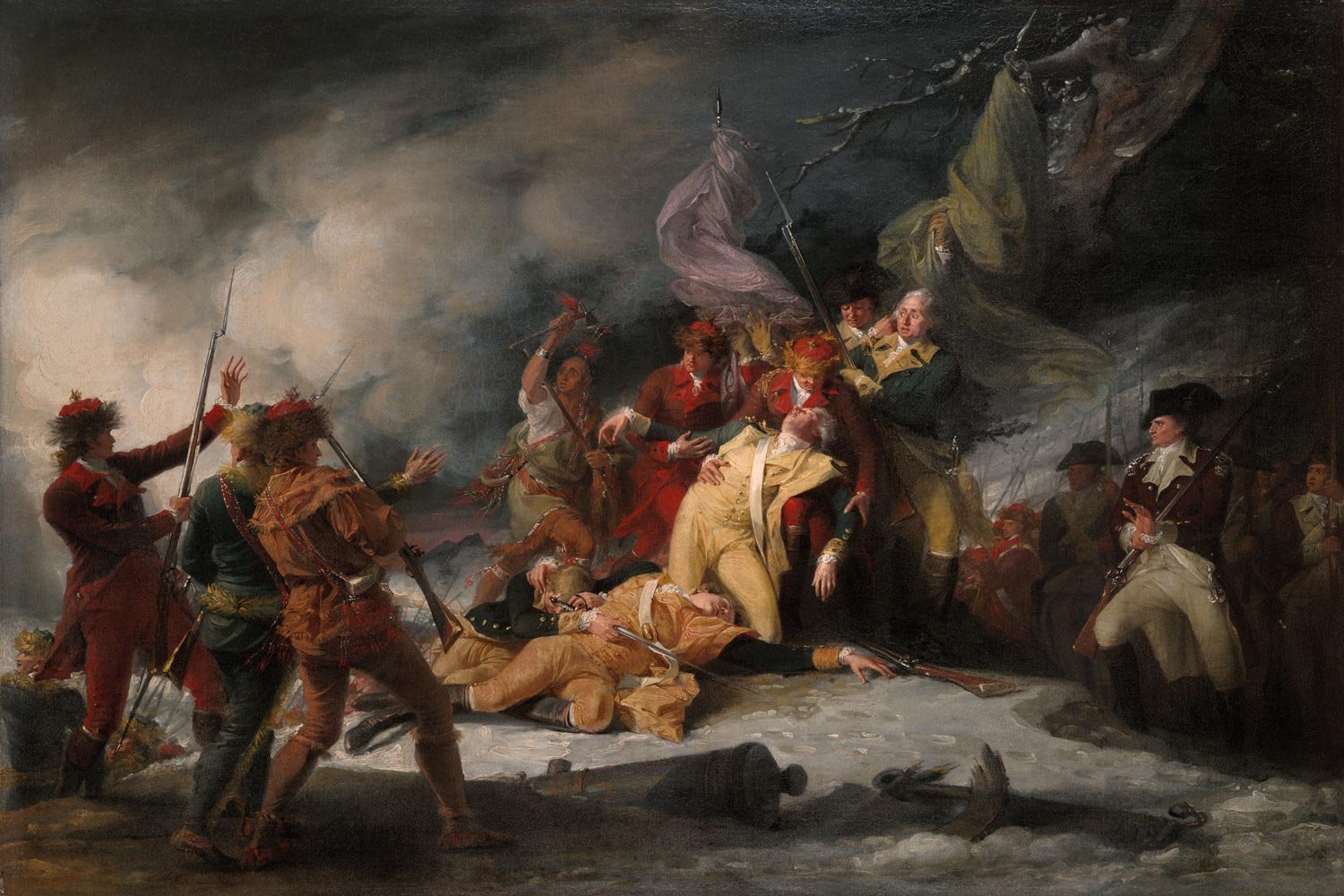

Assault on Quebec Ends in Disaster
On December 26, General Richard Montgomery assembled the key officers in his army besieging Quebec City to discuss their next steps. The bombardment of the city had failed to convince British General Guy Carleton to surrender and there were only five days remaining until the enlistments of most of Montgomery’s men expired and they left for home. There was grumbling in the ranks that the retreat should have already started.




