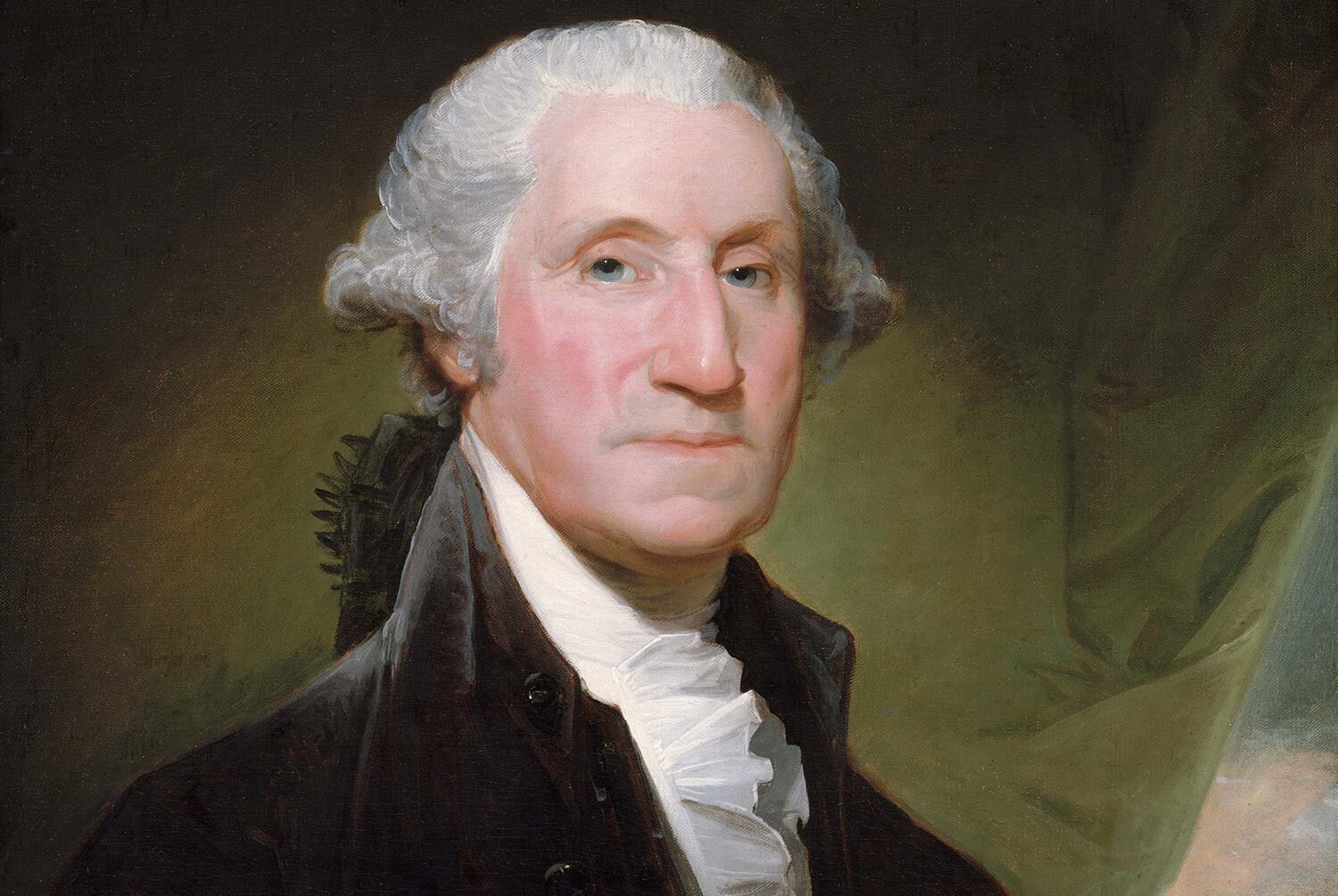
George Washington, Our Nation’s First President
The federal Constitution, the new law of the land, took effect on March 4, 1789, and had several notable differences with the Articles of Confederation. One of the most significant changes was the creation of a strong executive or President. However, the powerful executive reminded skeptics of the authority held by King George, and they worried the United States could eventually drift towards despotism. Virtually everyone knew that the only man strong enough to lead the nation and conscientious enough to be entrusted with so much power was George Washington.

The Constitution of the United States
The opening phrase of the preamble, “We the People,” spoke volumes regarding upon whose authority the Constitution rested and suggested the unanimity of country and purpose that this new Constitution would create. It was written by Gouverneur Morris, a delegate from New York, and his eloquent words speak for themselves.
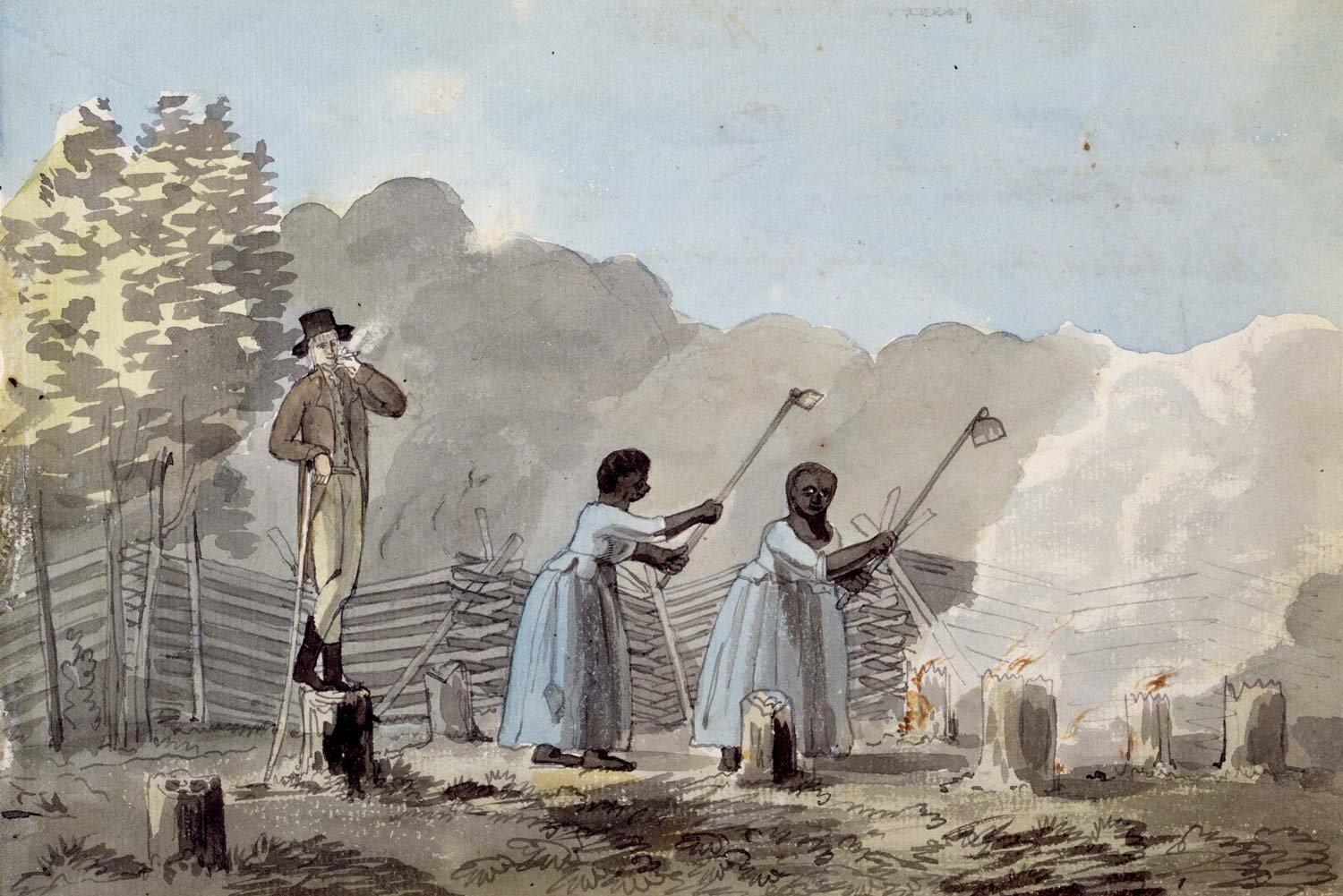

The Slavery Question at the Constitutional Convention
When delegates met at the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia in the summer of 1787, one of the most troublesome questions was what to do about slavery. Not whether it should be abolished, because even the most vehement abolitionist recognized this was neither the time nor the place for that fight. The issues to be decided were how would slaves be counted in the census and whether the states or the central government would control the institution, and what that control would look like.

Key Debates at the Constitutional Convention
On May 29, 1787, Edmund Randolph, Governor of Virginia, rose and introduced fifteen resolutions to the Federal Convention. Known to history as the Virginia Resolves or the Virginia Plan, Randolph’s proposal, which was probably drafted by James Madison, was an outline for an entirely new national government. It called for a national executive, a two-house national legislature, and a national judiciary.

The Federal Convention Opens
In the years immediately following the successful conclusion of its war for independence, the United States struggled to survive under the Articles of Confederation. The nation’s leaders knew something had to be done to fix its many issues for this great experiment in democracy to continue.
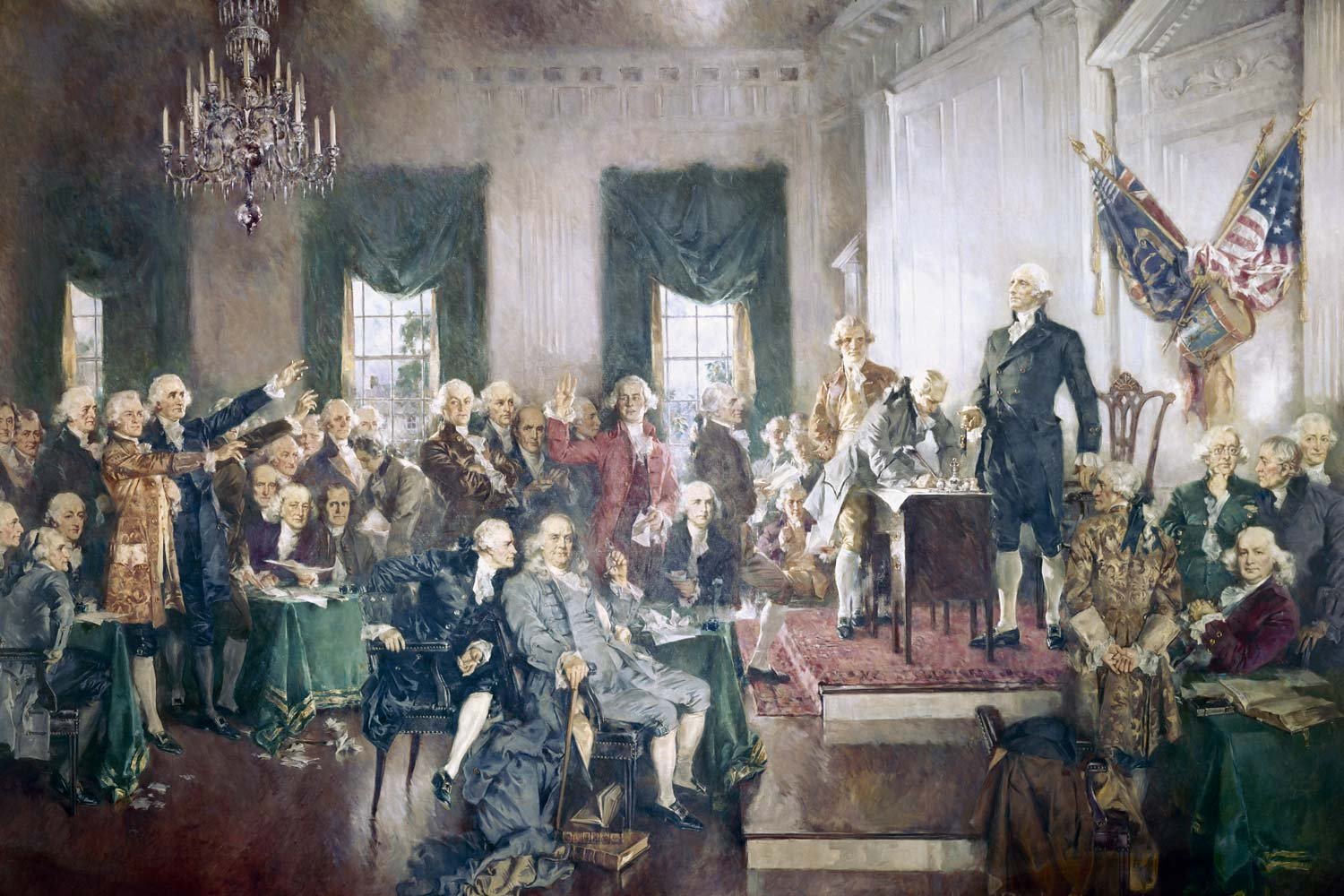

Ben Franklin’s Sage Advice Influences Constitutional Convention
In 1785, Franklin, his work done in France, was recalled to America by Congress. He arrived in Philadelphia that September, revered as one of our nation’s greatest patriots. Despite his need for a well-deserved rest, he was kept continually busy receiving dignitaries, wrapping up loose ends from his eight-year diplomatic mission, and with what would prove to be one final opportunity to help his country.

The Quasi-War and Its Aftermath
The only fighting in the Quasi-War occurred at sea, and mostly in the Caribbean. But with war at a fever pitch and French interests so close by in Louisiana, there was a very real concern in Congress about a possible French invasion of the United States from the west.
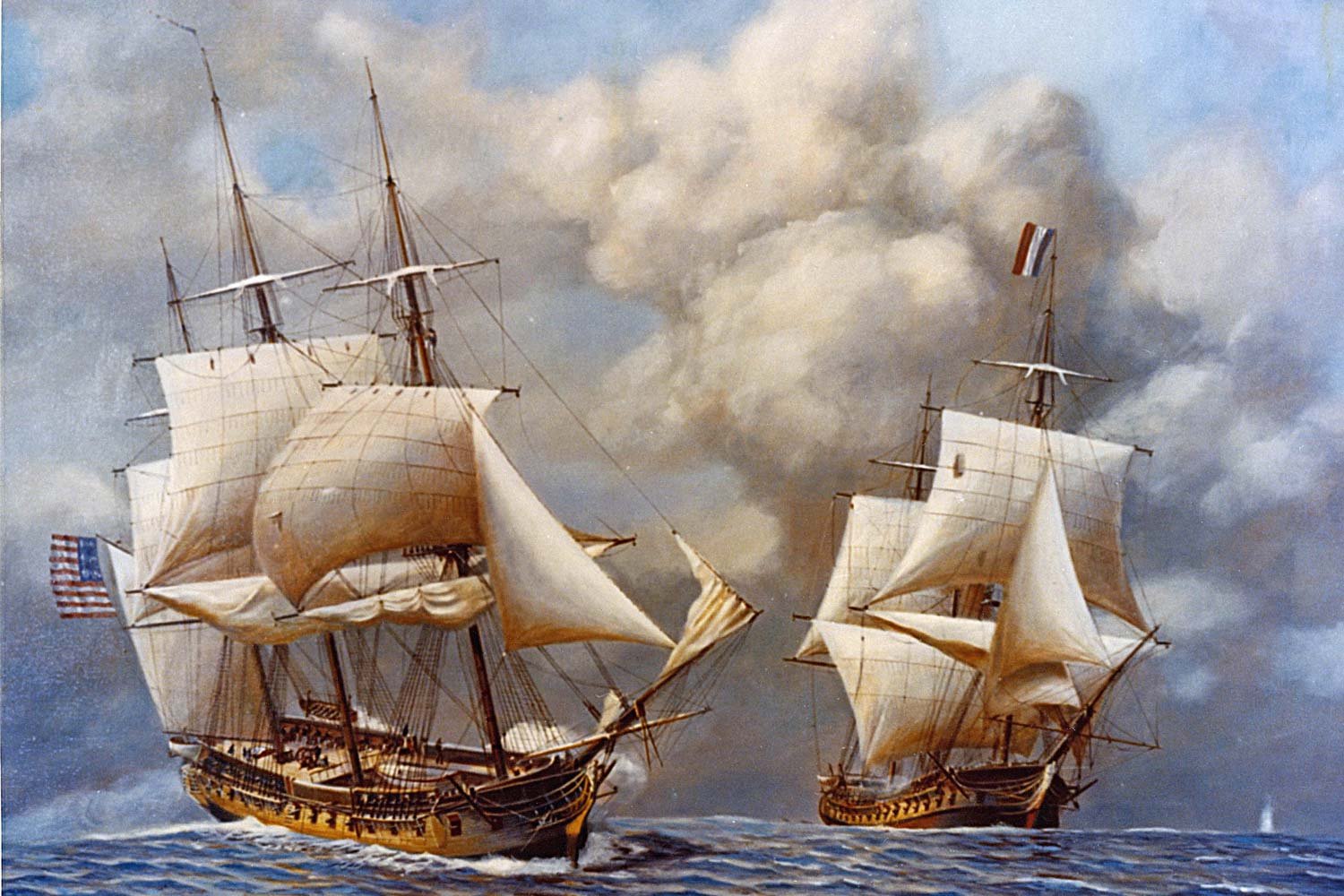

Escalating Tensions with France Lead to Quasi-War
The Quasi-War was an undeclared war between France and the United States, largely fought at sea in the Caribbean and along the southern coast of America, between 1798 and 1800. It developed because of a series of related events that soured the formerly strong relationship between the two nations.
Relations Between America and France Fall Apart
America’s first armed conflict with a foreign nation following our Revolution was not the War of 1812, but rather a mostly forgotten fight called the Quasi-War. Although little known today, in its time it made a significant impact on the course of American history, affecting trade, the creation of our Navy, and a presidential election.

The Inspiring Legacy of John Adams
John Adams lost the Presidential election of 1800 to Thomas Jefferson after a bitter fight. Adams was terribly disappointed as felt he deserved another term, but he accepted the verdict of the Electoral College.
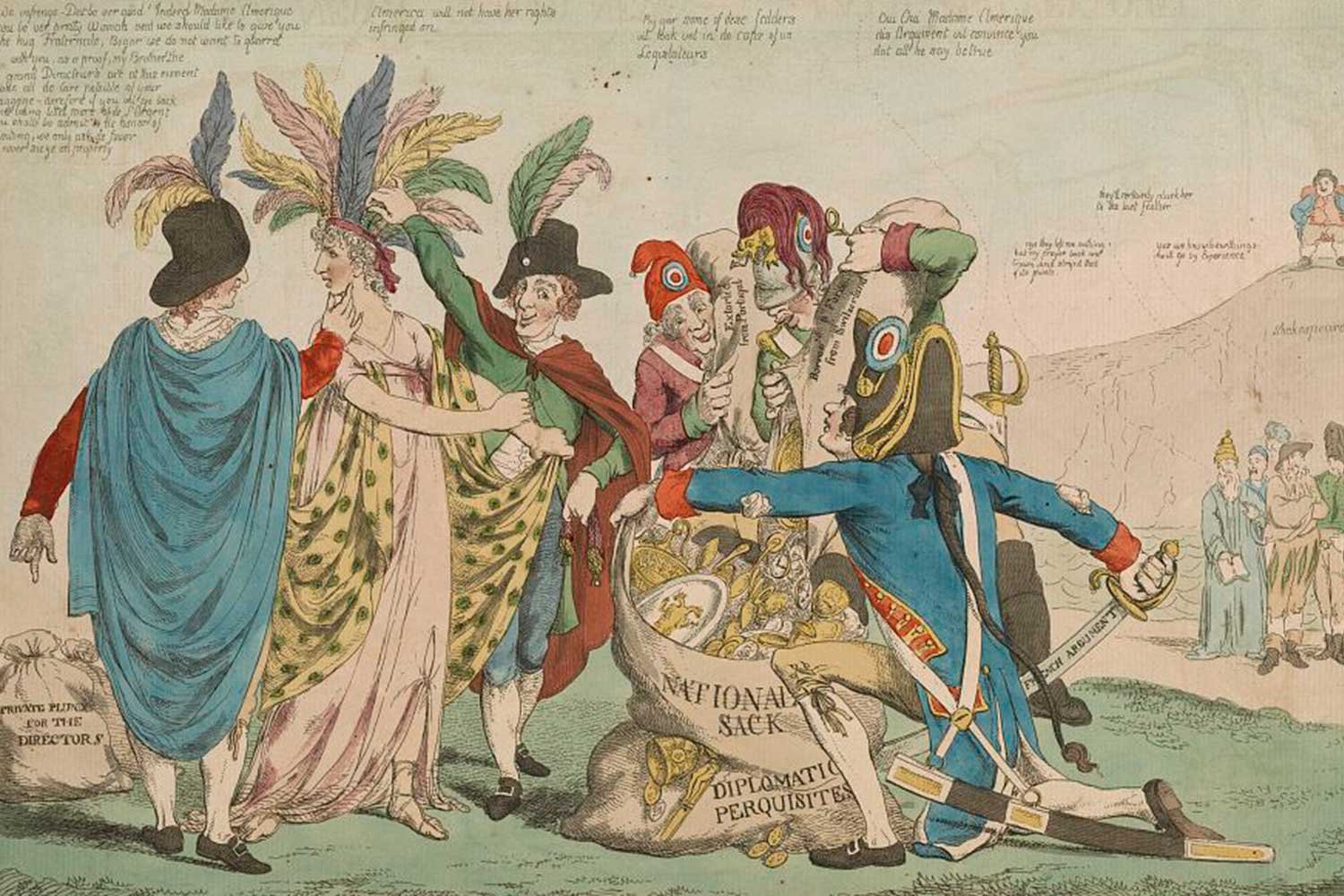

The Presidency of John Adams
To avoid a war with France, in 1797, President John Adams sent a diplomatic delegation to Paris to calm rising tensions. When our team arrived in France in October 1797, they were approached by three French officials whose code-names were X, Y, and Z. These Frenchmen demanded large bribes from the Americans for themselves and other French officials before negotiations could start.

John Adams and the Presidential Election of 1796
After eight years as Vice President under George Washington, John Adams hoped to succeed the Father of our Country as President of the United States. His successful election in 1796 gave him his chance.