

The Quasi-War and Its Aftermath
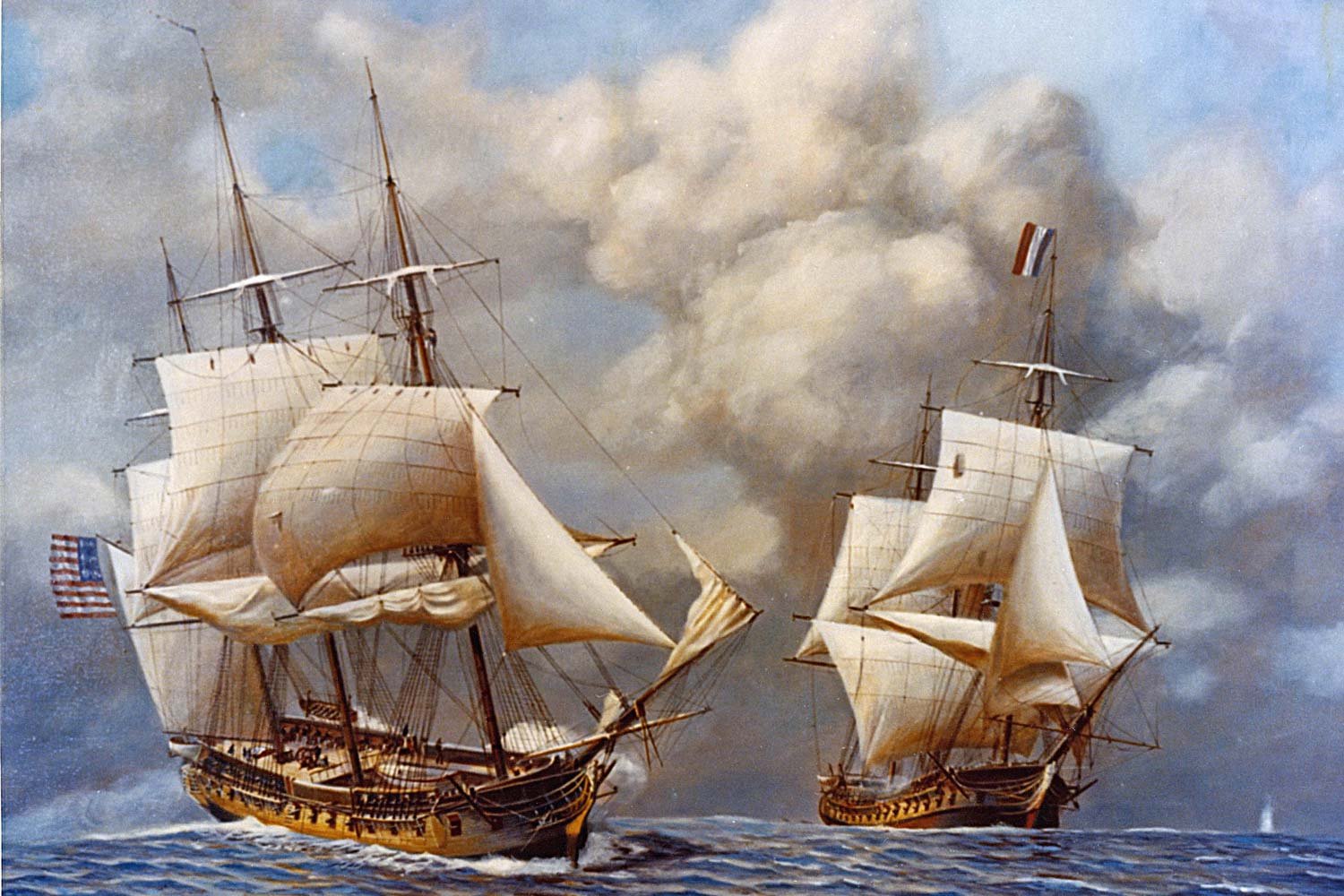
The only fighting in the Quasi-War occurred at sea, and mostly in the Caribbean. But with war at a fever pitch and French interests so close by in Louisiana, there was a very real concern in Congress about a possible French invasion of the United States from the west.

Escalating Tensions with France Lead to Quasi-War
The Quasi-War was an undeclared war between France and the United States, largely fought at sea in the Caribbean and along the southern coast of America, between 1798 and 1800. It developed because of a series of related events that soured the formerly strong relationship between the two nations.
Relations Between America and France Fall Apart
America’s first armed conflict with a foreign nation following our Revolution was not the War of 1812, but rather a mostly forgotten fight called the Quasi-War. Although little known today, in its time it made a significant impact on the course of American history, affecting trade, the creation of our Navy, and a presidential election.
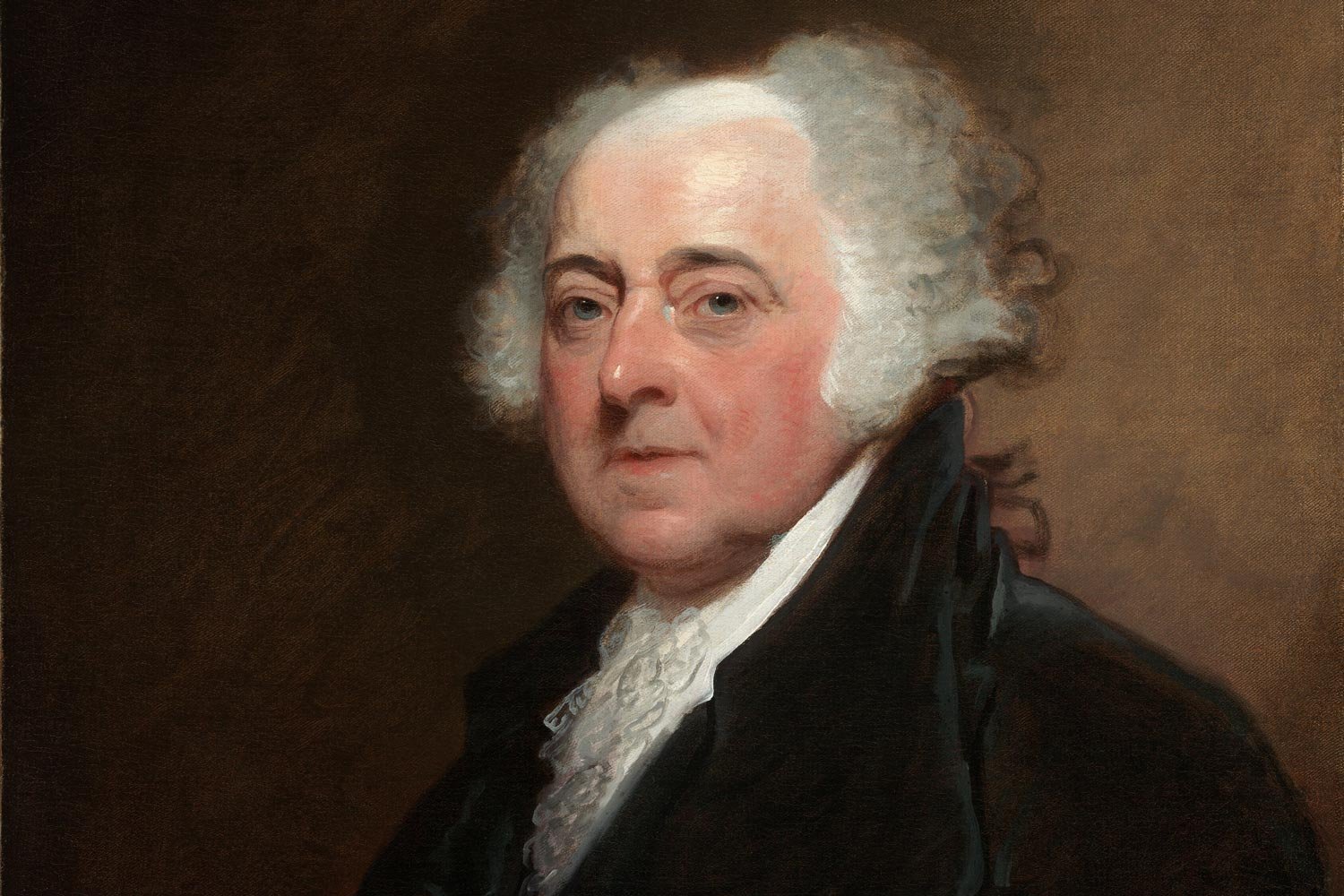

The Inspiring Legacy of John Adams
John Adams lost the Presidential election of 1800 to Thomas Jefferson after a bitter fight. Adams was terribly disappointed as felt he deserved another term, but he accepted the verdict of the Electoral College.

The Presidency of John Adams
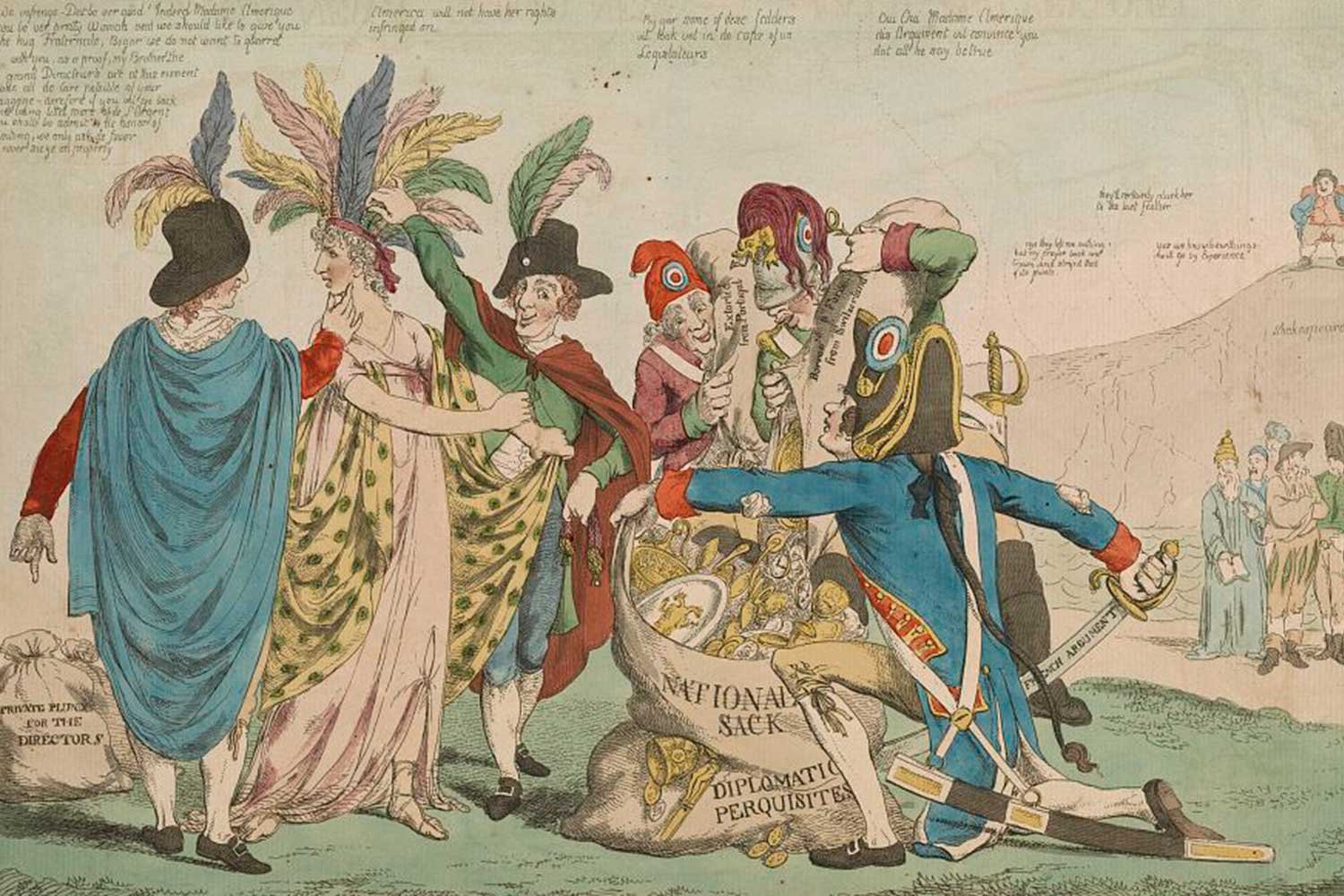
To avoid a war with France, in 1797, President John Adams sent a diplomatic delegation to Paris to calm rising tensions. When our team arrived in France in October 1797, they were approached by three French officials whose code-names were X, Y, and Z. These Frenchmen demanded large bribes from the Americans for themselves and other French officials before negotiations could start.
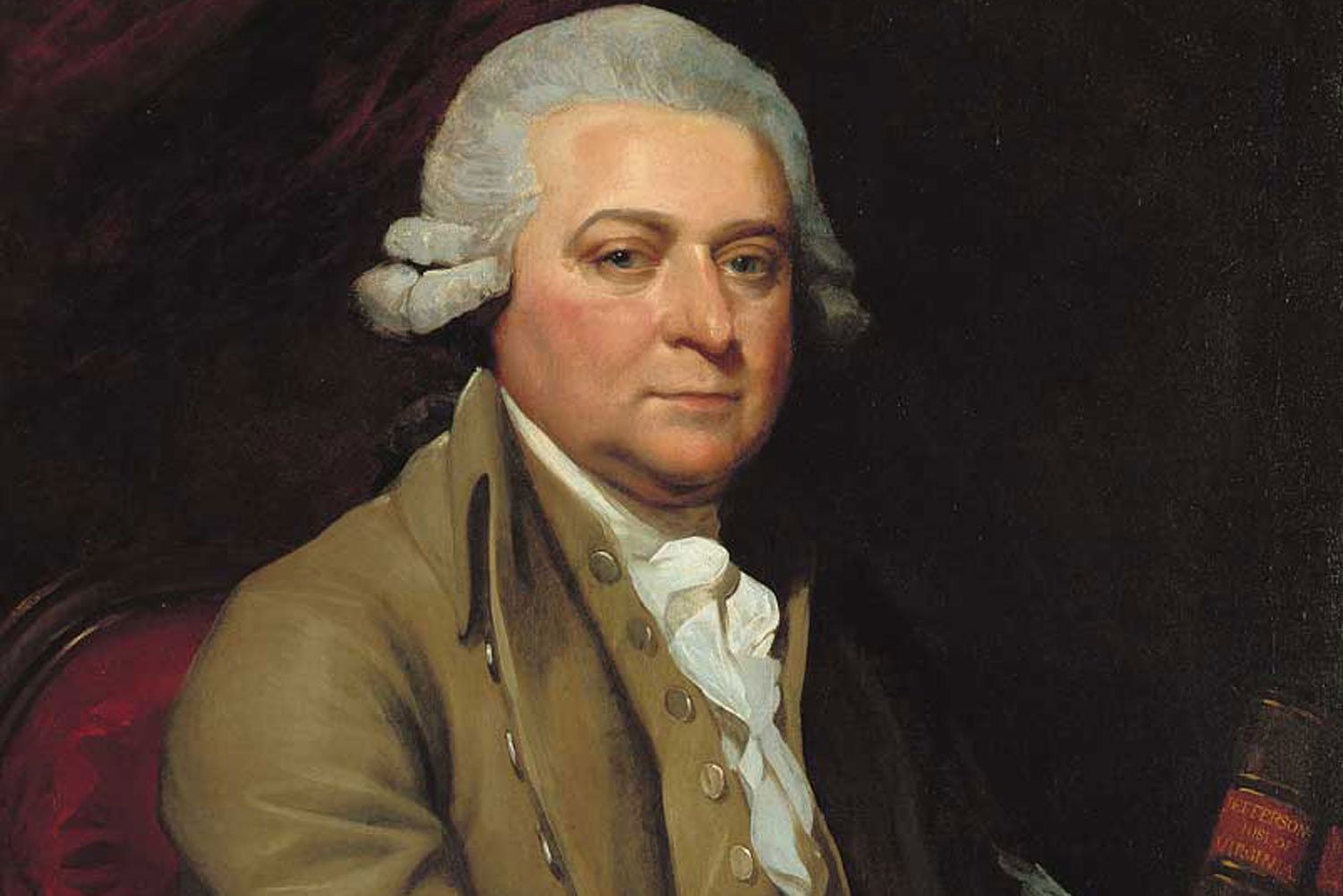

John Adams and the Presidential Election of 1796
After eight years as Vice President under George Washington, John Adams hoped to succeed the Father of our Country as President of the United States. His successful election in 1796 gave him his chance.
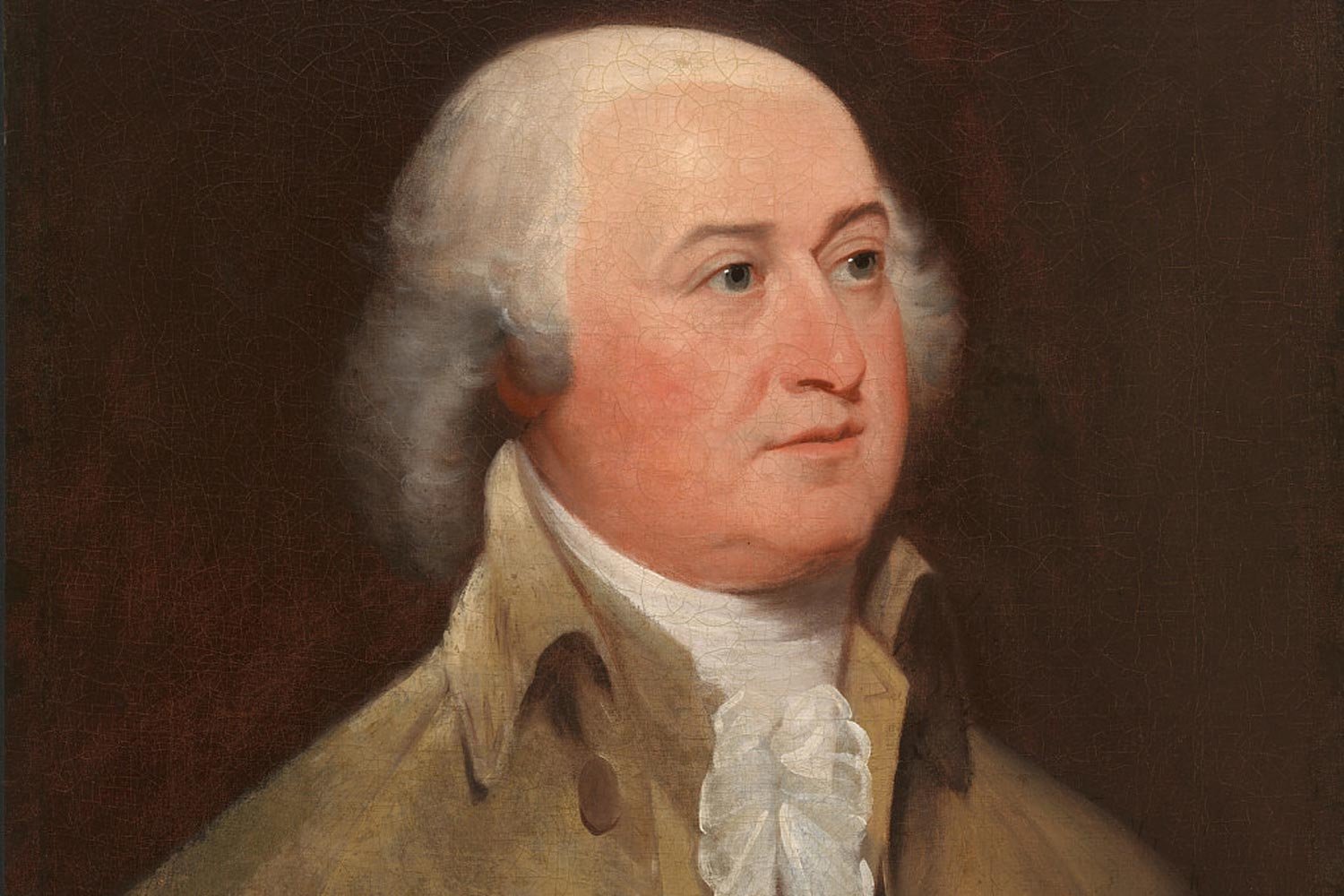

John Adams, Our First Vice President
John Adams was our nation’s first Vice President and helped shape the responsibilities of the office. Moreover, as the tie-breaking vote in the Senate, Vice President Adams was instrumental in passing several key pieces of legislation and establishing important precedents.
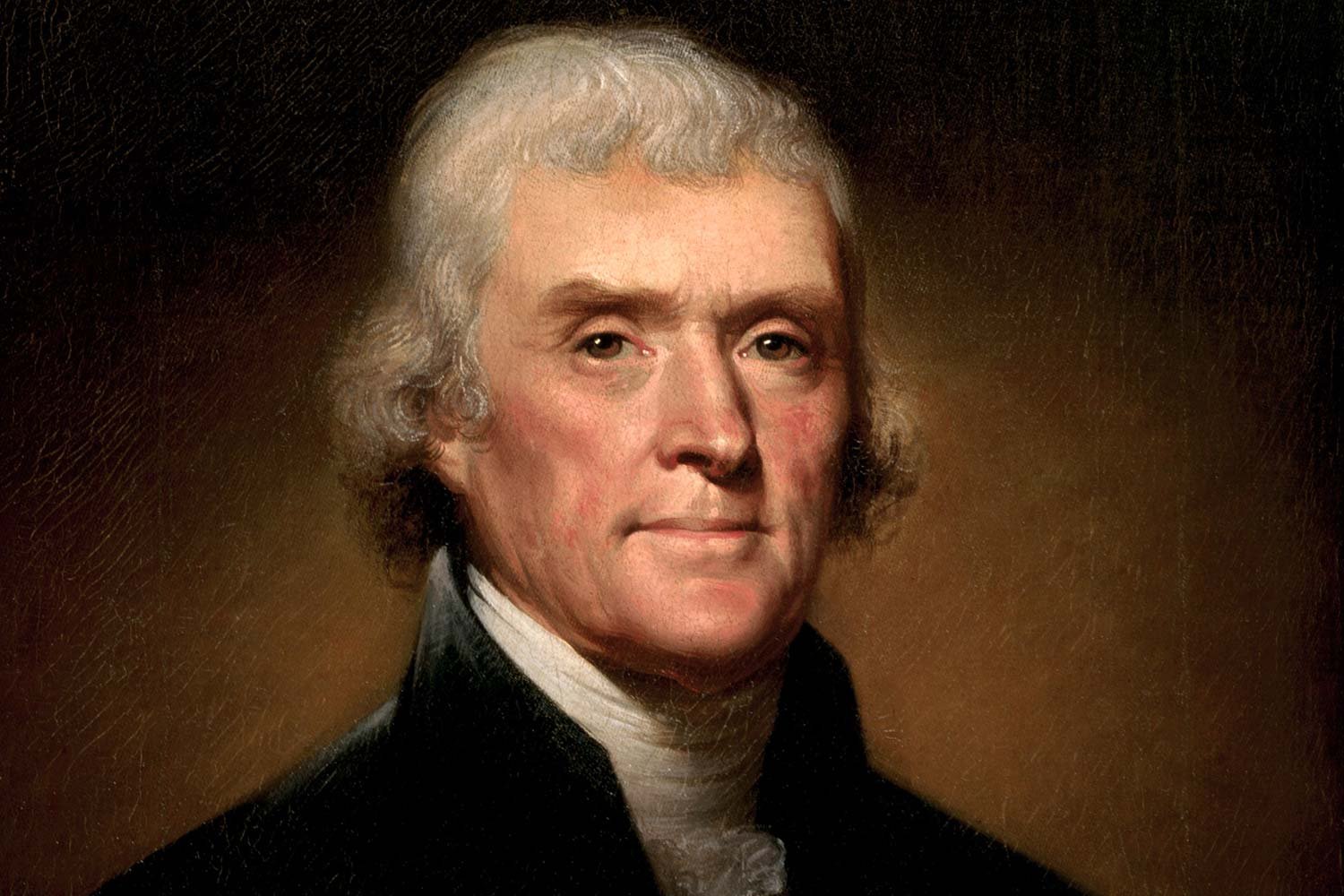

America’s “Era of Good Feelings” Comes to an End
When President George Washington retired in 1796, he devoted much of his Farewell Address to warning his fellow citizens about the danger of forming political parties. Unfortunately, the politicians did not listen.
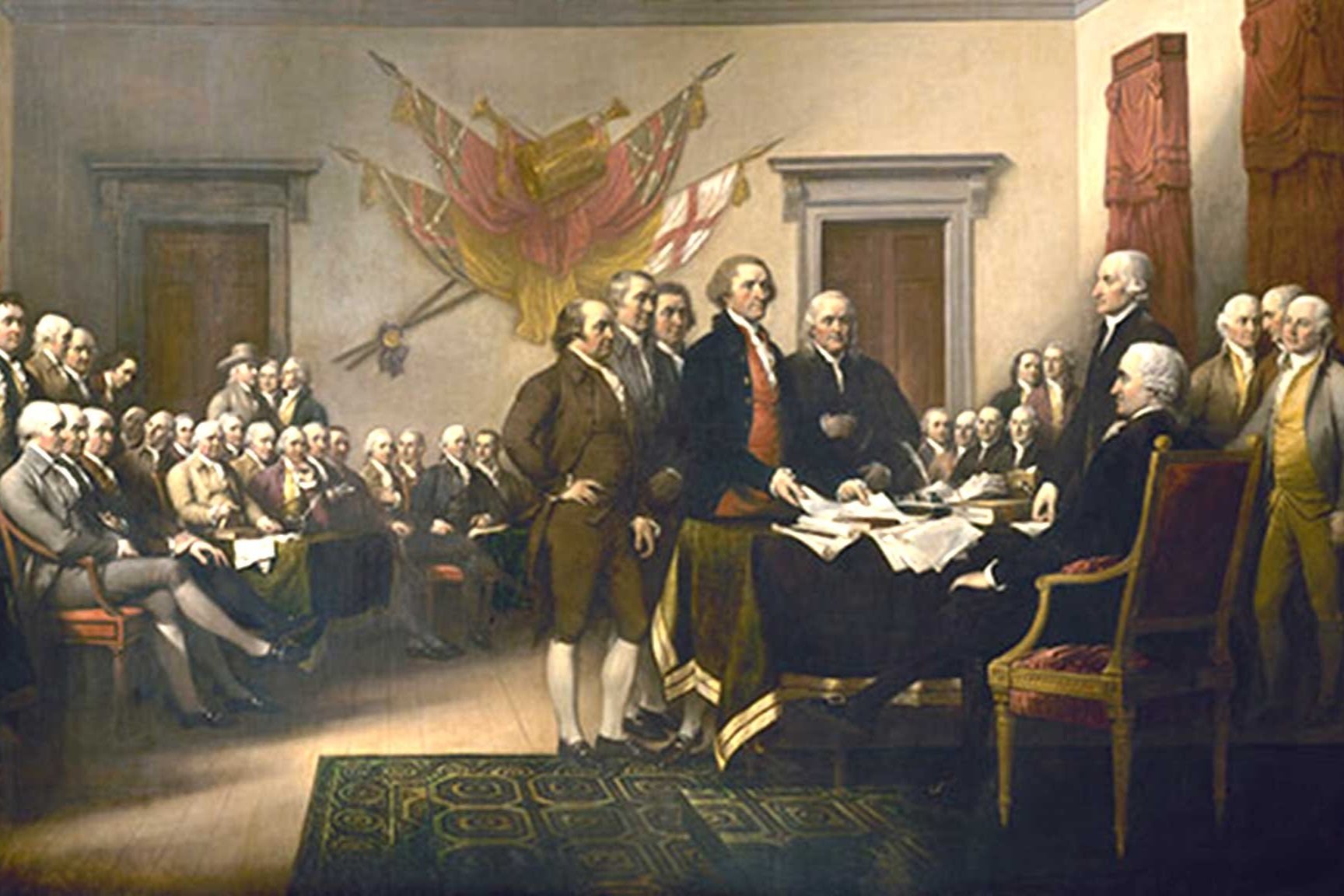

America’s Founding Era, A Time of Political Unity
During America’s founding era, our country was more politically unified than at any other time in our nation’s history. That is not to say politicians did not squabble because they did. The unity was reflected in the lack of political parties at first and then essentially having only one party for a quarter of a century.
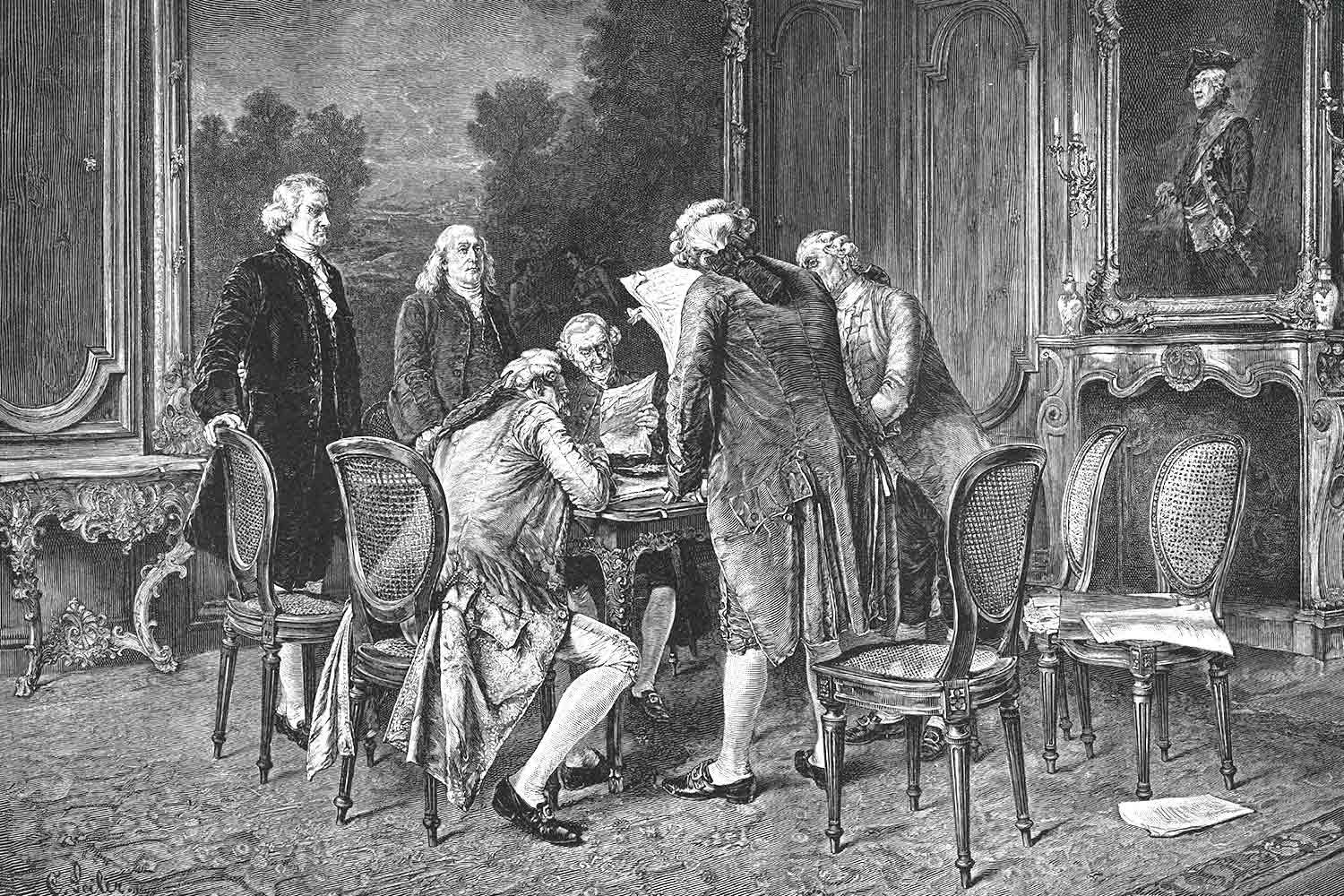

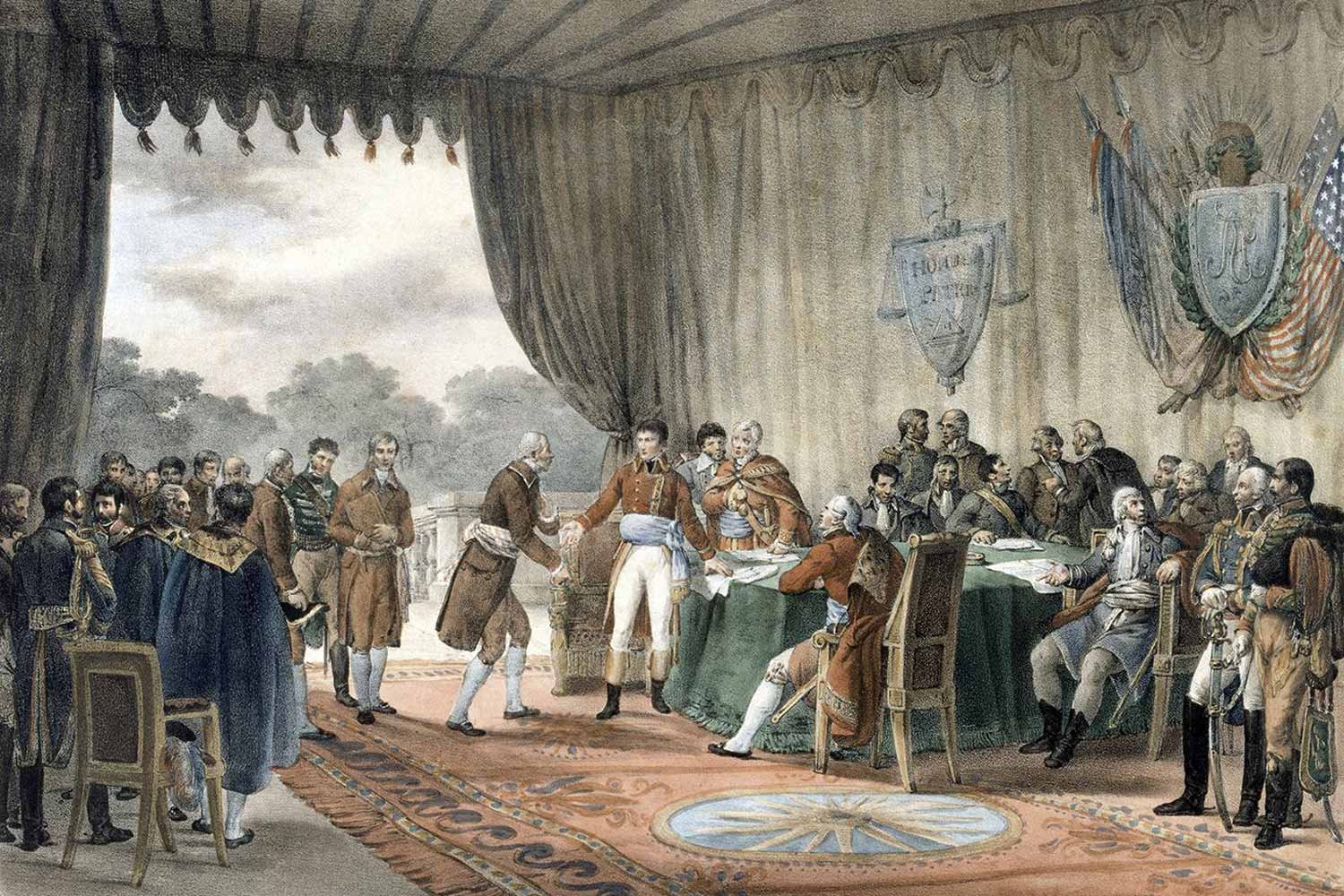
John Adams Negotiates Peace with England
John Adams was solely responsible for opening a strong relationship with the Netherlands between 1780-1782. Within days of completing his work in Amsterdam, Adams received a summons from John Jay, another American diplomat in Paris, to immediately return to the French capital. Peace talks with the English were heating up and Jay wanted Adams’ assistance.
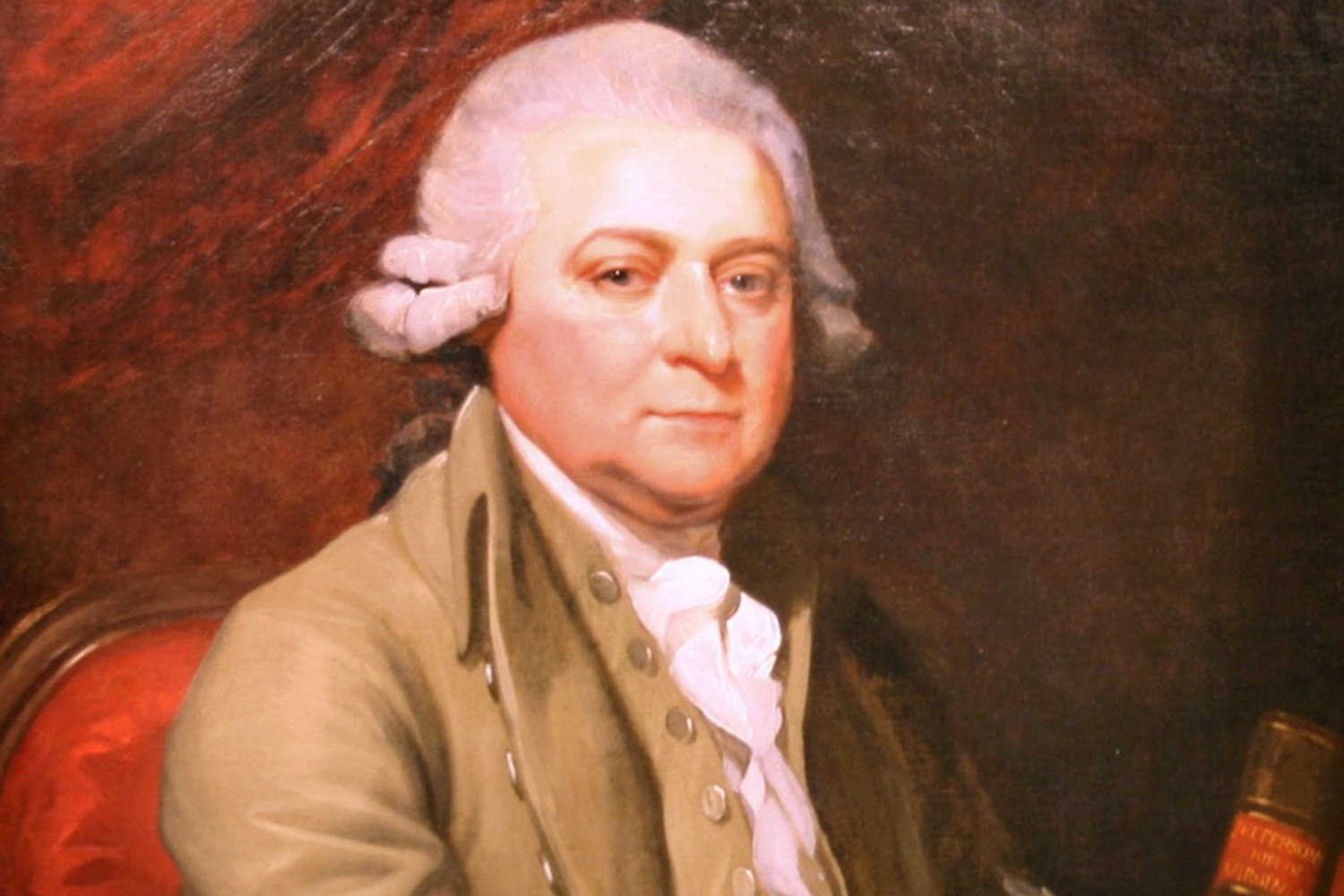

John Adams, A Diplomat in Europe
John Adams retired from the Second Continental Congress in early November 1777 and returned home to Braintree. He hoped to revive his law practice and enjoy some quiet time with Abigail and the rest of the family. However, his stay was short-lived as America had another task in mind for this tireless patriot, this time as an ambassador in Europe.

Thomas Paine’s Common Sense Inspires a Nation
The literary work most often credited with inspiring the American Revolution was a 47-page pamphlet called Common Sense. Published on January 10, 1776, and written by Thomas Paine, a recent immigrant from England, it caused everyday Americans to begin seriously thinking about an independent United States.




