Settling the Ohio Frontier
In the 1780s, American pioneers began moving into the Ohio frontier and met resistance from Indian tribes who claimed the land as their own. The clash between these two disparate cultures resulted in the Northwest Indian War, the first war ever fought by the new constitutional government. Determined to protect the pioneers and encourage settlement, President Washington tried to purchase land from the tribes rather than committing to an expensive war. In January 1789, Territorial Governor Arthur St. Clair convinced several chiefs to sign the Treaty of Fort Harmar, which essentially ceded all of Ohio to the United States. But the Shawnee, encouraged by promises of British support, refused to sign the treaty or acknowledge its legitimacy.
Tom Hand, creator and publisher of Americana Corner, explores the clash between settlers and Indian tribes on the Ohio frontier, and why it still matters today.
Images courtesy of Encyclopedia Virginia, Library of Congress, The New York Public Library, Digital Commonwealth, National Gallery of Art, National Archives, University of South Florida, Alamy, Picryl, National Portrait Gallery - Smithsonian Institution, Wikipedia.

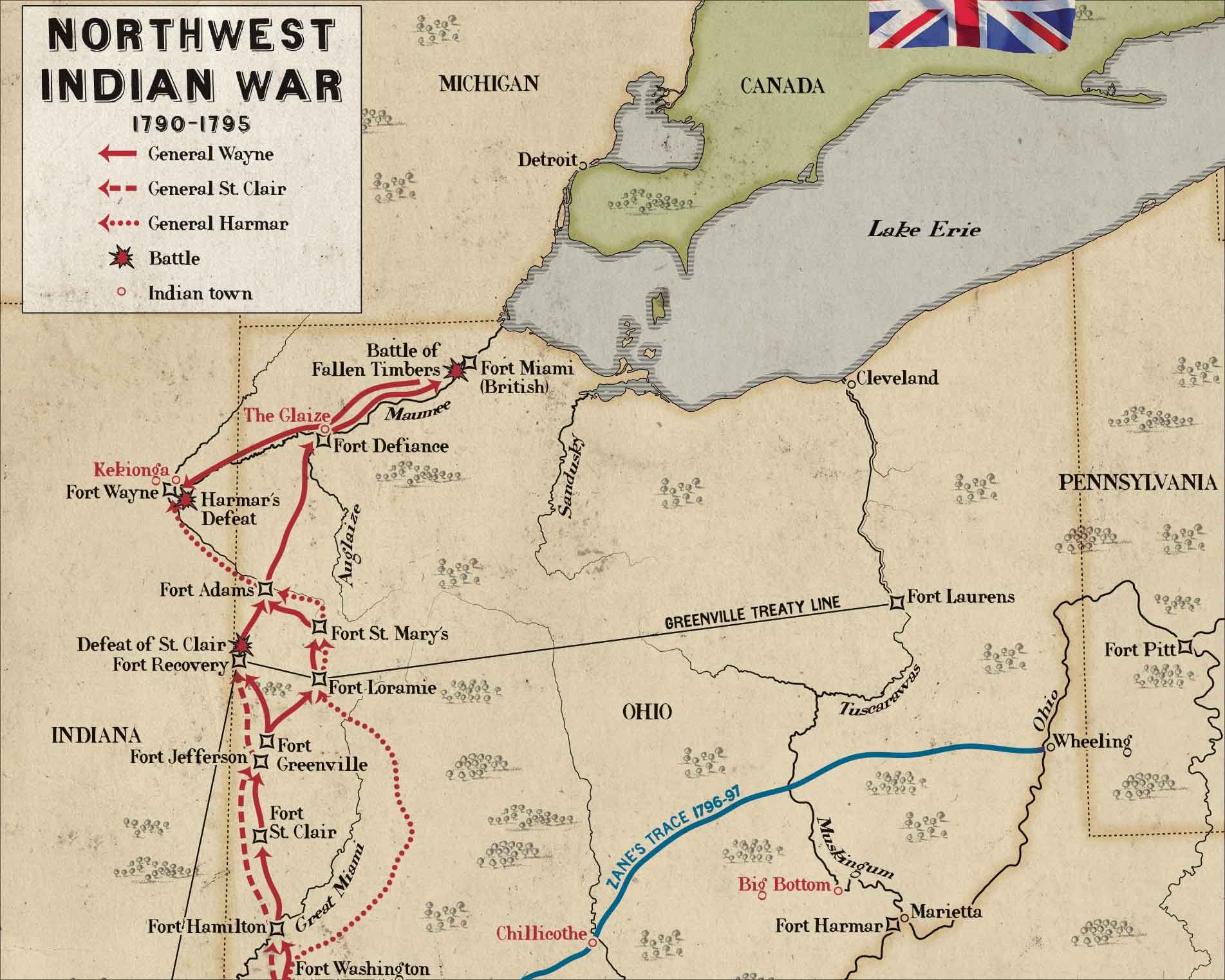
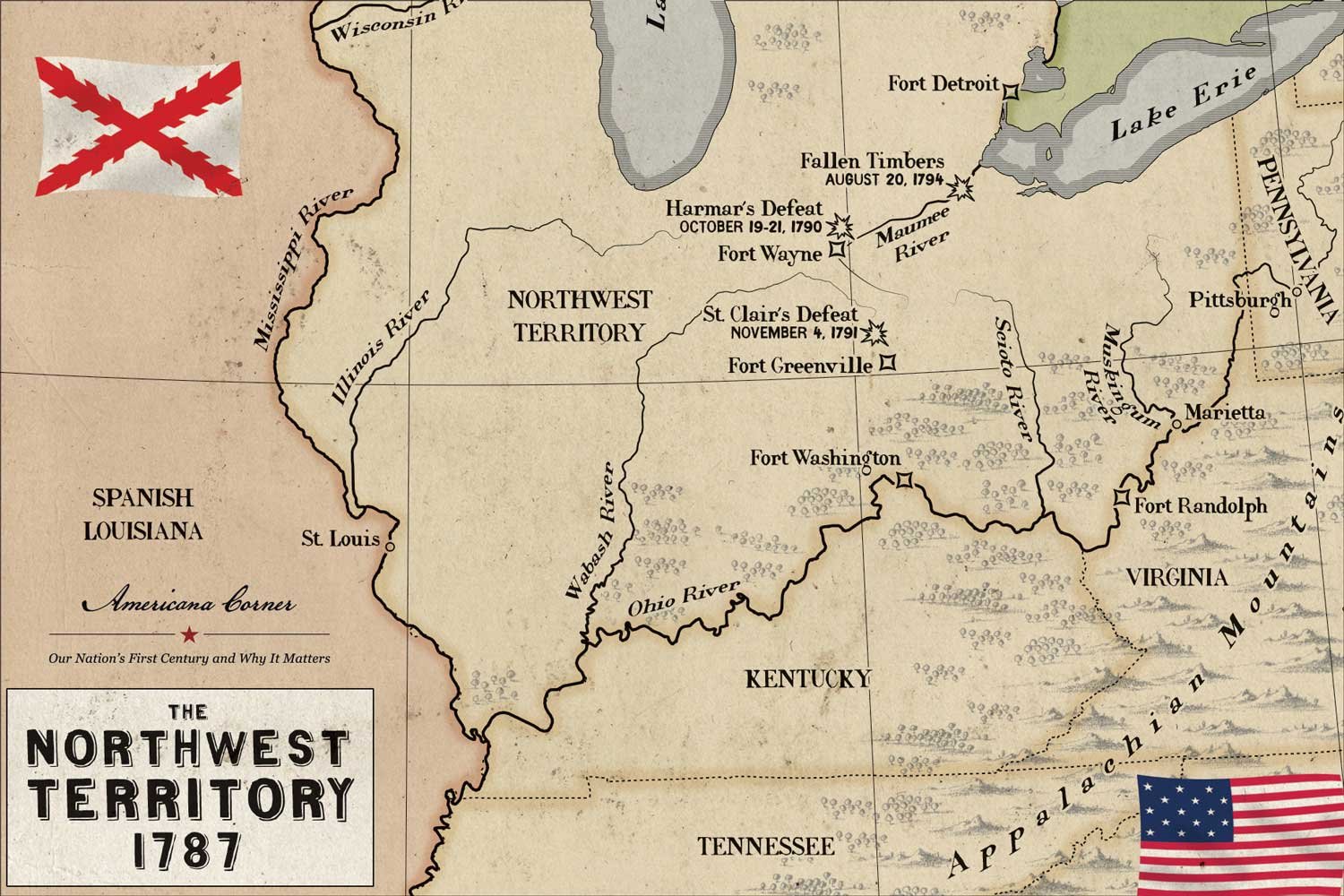

The American army commanded by General Josiah Harmar had been badly mauled by the Northwestern Confederacy in the autumn of 1790. Anxious to demonstrate the will and ability to gain control of the Ohio Country, the following March, Congress expanded the army to two regiments and President George Washington appointed Arthur St. Clair, the Governor of the Northwest Territory, to command the new force.