American Judiciary, Part 10: The Treason Trial of Aaron Burr
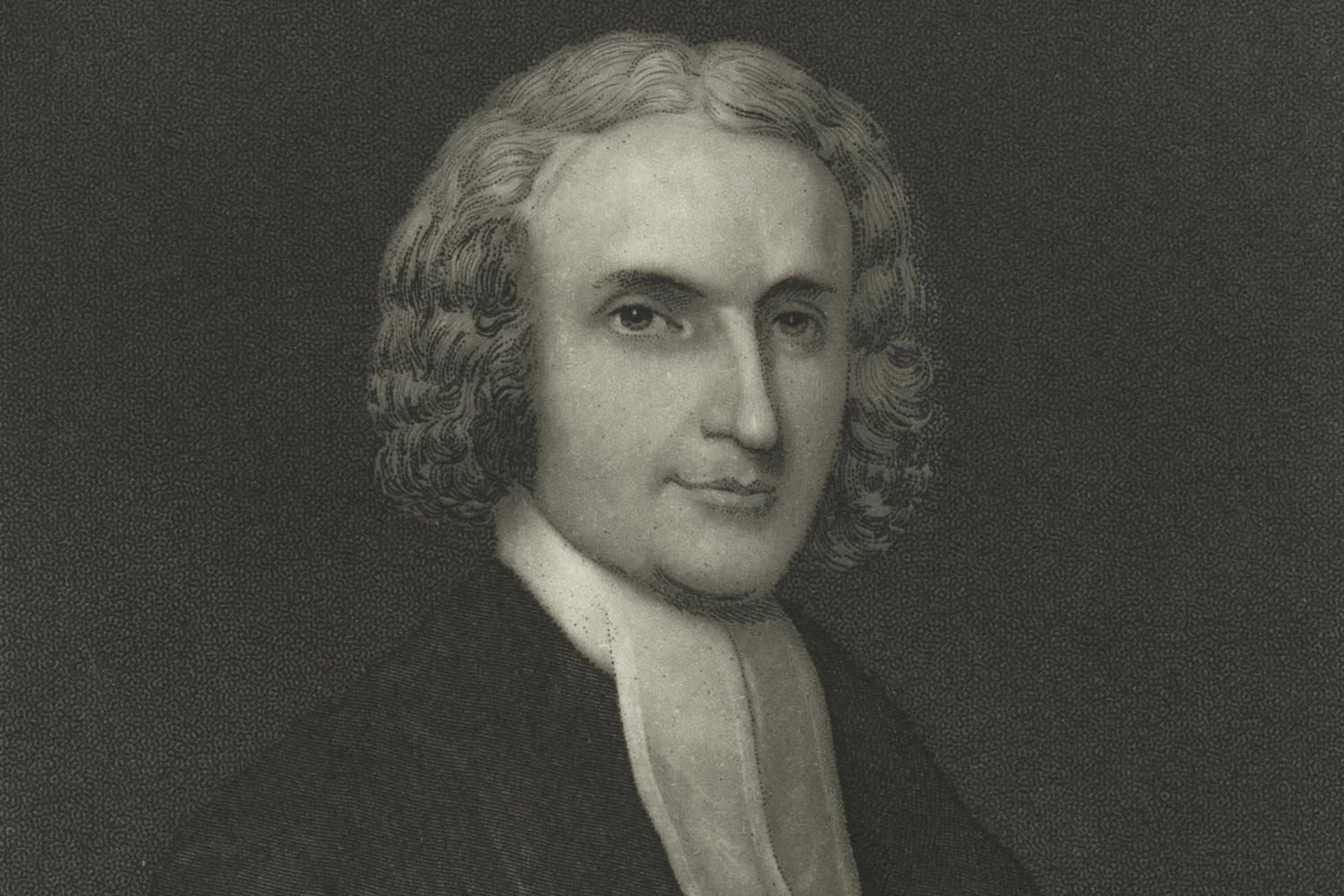
On May 22, 1807, Aaron Burr was brought before a grand jury in Richmond, Virginia, charged with committing treason against the United States. The prosecution’s star witness, General James Wilkinson, proved to be a liability as Wilkinson was forced to admit that he had forged a letter from Burr which was the prosecution’s main piece of evidence. Regardless, the grand jury, made up mostly of Democratic-Republicans, indicted Burr for treason, the only time in our country’s history when a President or Vice President has been indicted for this crime.
American Judiciary, Part 9: The Burr Conspiracy
In the presidential election of 1800, Aaron Burr and Thomas Jefferson tied for the most electoral votes, but Burr refused to stand aside for Jefferson. The House of Representatives ultimately selected Jefferson to be president and Burr vice president, but Burr’s decision to challenge Jefferson made him an arch enemy of the president and an outcast in the Democratic-Republican party. Upon leaving office in the spring 0f 1805, Burr was a ruined man, financially and politically, with his reputation in tatters.
American Judiciary, Part 8: The Impeachment of Samuel Chase
Samuel Chase is the only Supreme Court Justice in our nation’s history to be impeached and that occurred during a political tussle over the independence and power of the judiciary between President Thomas Jefferson and Chief Justice John Marshall. In March 1804, the House of Representatives, in a party line vote, approved eight charges of impeachment against Chase. The problem was that the Constitution states that civil officers like Supreme Court justices may only be removed for “Treason, Bribery, or other high Crimes and Misdemeanors” and Chase was not charged with any of these. But that was just the point; the Chase trial was part of a larger Democratic-Republican plan to reduce the power and independence of the judiciary.
Lewis and Clark Expedition, Part 3: Leaders of the Corps of Discovery
In March 1801, Captain Meriwether Lewis received a letter from Thomas Jefferson, the newly inaugurated president and a family friend, asking Lewis to become his private secretary. At the time, Lewis was a twenty-seven-year-old captain serving as the paymaster for the First Infantry Regiment. Over the next two years, Jefferson tutored Lewis on the lands west of the Mississippi and in the sciences of astronomy, botany, and anatomy in anticipation of an exploratory expedition to the Pacific Ocean. But both Jefferson and Lewis recognized the need to find a capable second officer for the expedition, and the man Lewis wanted to fill this coveted position was William Clark.
Lewis and Clark Expedition, Part 2: Thomas Jefferson’s Western Vision
In 1803, President Thomas Jefferson drafted his official instructions for a great expedition to explore the Louisiana Territory and asked his private secretary, Captain Meriwether Lewis, to lead it. Once assembled, the Corps of Discovery would operate like a small frontier garrison with rigidly maintained discipline. In the end, the group went forward remarkably prepared for what they would encounter over the next few years, a testament to the thorough planning of President Jefferson.
An Expression of the American Mind
On June 7, 1776, Richard Henry Lee introduced into the Second Continental Congress what has come to be known as the Lee Resolution, calling for a complete separation from Great Britain. This leap of faith into the unknown space of independence finally had been publicly demanded and a contentious debate ensued. Congress created a committee to draft a declaration of independence in the event they chose that course of action. The committee included Benjamin Franklin, John Adams, Robert Livingston, Roger Sherman, and Thomas Jefferson, and chose Jefferson to be the main penman.
Thomas Jefferson’s “Summary View”
Thomas Jefferson’s revolutionary journey began in the 1760s and culminated in his masterfully written Declaration of Independence in 1776. But in between these events, Jefferson crafted one of the most impactful statements ever for American independence. Entitled A Summary View of the Rights of British America, it was perhaps the most logical assessment of the true relationship between Great Britain and her American colonies; concepts that Jefferson had refined over the course of several years.
Thomas Jefferson, the Virginia Barrister
n 1765, Parliament passed the Stamp Act, the first internal tax on the American colonies, and thus began a decade of missteps by the British. That same year, Thomas Jefferson concluded his time studying law under George Wythe and began his brief but successful law career. In colonial Virginia, there were two levels of courts – county courts, which were scattered throughout the colony, and the General Court of Virginia in Williamsburg. Jefferson opted to bypass the county courts and try for immediate admittance to the General Court. His brilliance recognized, Jefferson was accepted, and at age twenty-four, he joined a small group of much older attorneys considered the best in the colony, including George Wythe, Edmund Pendleton, and Richard Bland.
The Early Life of Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson was born on April 13, 1743, in a small farmhouse on the frontier of western Virginia, in today’s Albemarle County. His father, Peter Jefferson, was a mountain of a man and well-respected throughout the region as a surveyor who ranged far and wide over the western portions of the colony. Peter’s work brought him significant wealth and put him in contact with the leading authorities in the colony. Sadly, in the summer of 1757, when Tom was fourteen, his father got sick and passed away, leaving behind a widow and eight children and a sizeable, debt-free estate. One of his father’s dying wishes was for Tom to complete his education, and in March 1760, Jefferson entered the College of William and Mary in Williamsburg.
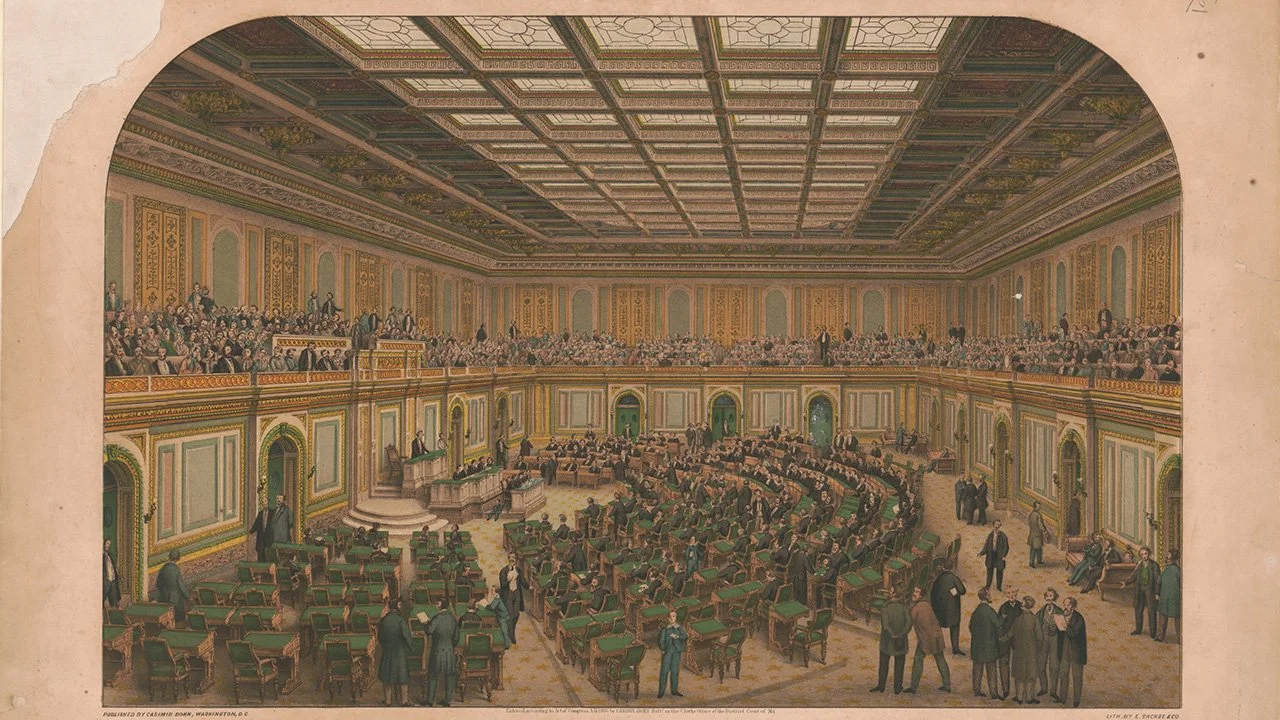
The House of Representatives Chooses Thomas Jefferson
The presidential election of 1800 ended in a tie, as the two Democratic-Republican candidates, Thomas Jefferson and Aaron Burr, each received 73 electoral votes. Burr had been added to the ticket to carry his home state of New York, but it was assumed that nationally Jefferson would get the most votes and Burr the second most. When that did not happen, the election moved to the United States House of Representatives in accordance with Article 2, Section 1 of the Constitution.
The Election of 1800
The presidential election of 1800 was one of the most controversial and consequential in the history of the United States. It represented a true changing of the guard as the Federalist party of Washington, Hamilton, and Adams gave way to the Democratic-Republican ideals of Jefferson and Madison and took the United States in a different direction for a generation to come.
The Election of 1796
The first contested United States presidential election took place in the fall of 1796, pitting Thomas Jefferson against Vice President John Adams. Arguably, no presidential election in the country’s history has ever featured a choice between two such American titans. Jefferson was the leader of the Democratic-Republicans who were pro-French and favored strong states’ rights. Adams was the favorite son of the Federalist Party that was pro-British and favored a strong central government. For the most part, the election split along geographic lines with Adams capturing the north and Jefferson the southern states, plus Pennsylvania.