
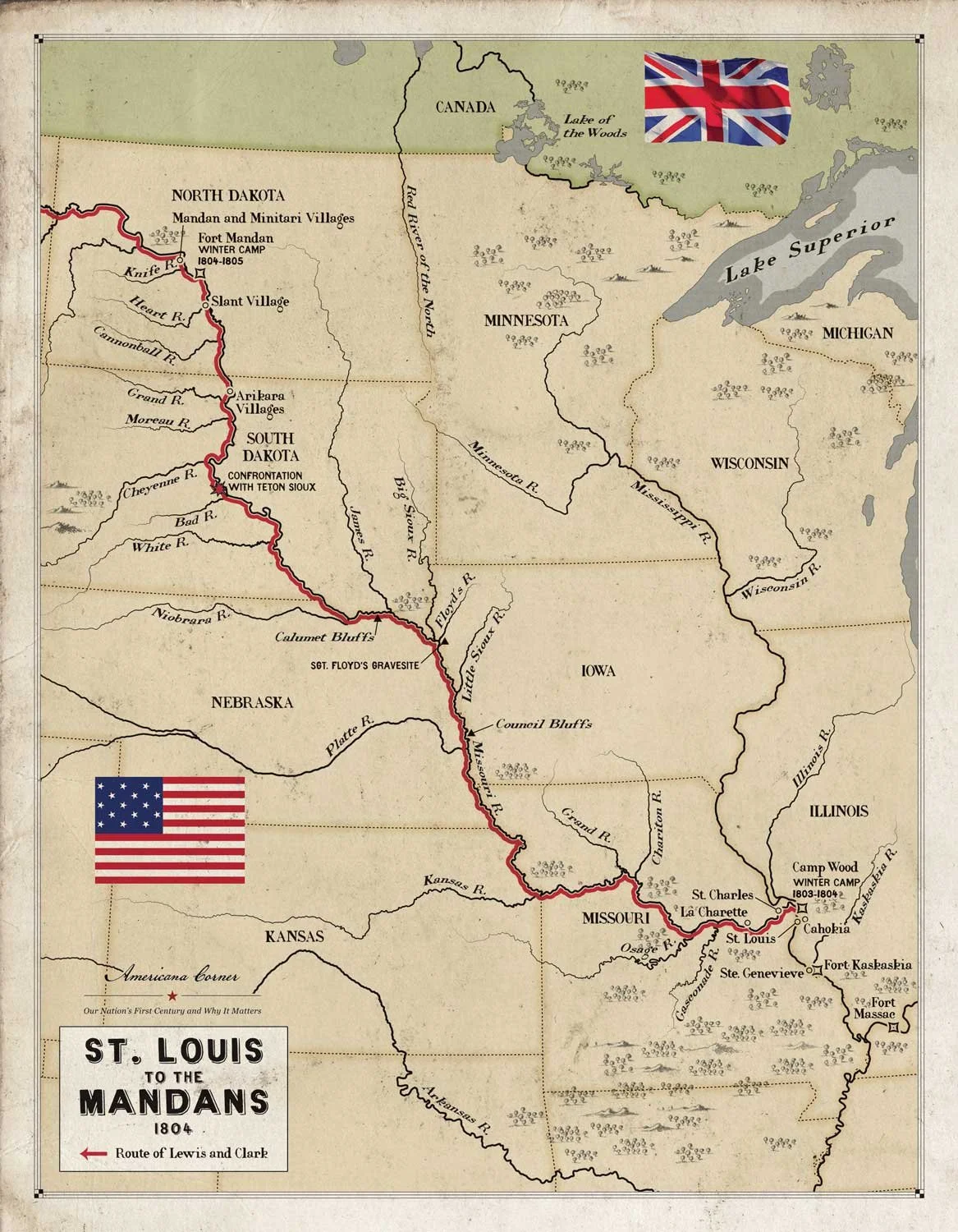
Lewis and Clark Expedition, Part 4: Lewis and Clark Leave Civilization Behind
On August 31, 1803, Captain Meriwether Lewis departed from Fort Fayette, today’s Pittsburgh, in the keelboat the Corps of Discovery would take up the Missouri River and, six weeks later, arrived at the Falls of the Ohio and Clarksville, Indiana Territory. It was here, at the town founded by General George Rogers Clark, that Meriwether Lewis and William Clark, the General’s youngest brother, met again for the first time in seven years and commenced the most famous partnership in American history, two men so joined in American lore as to almost be inseparable.
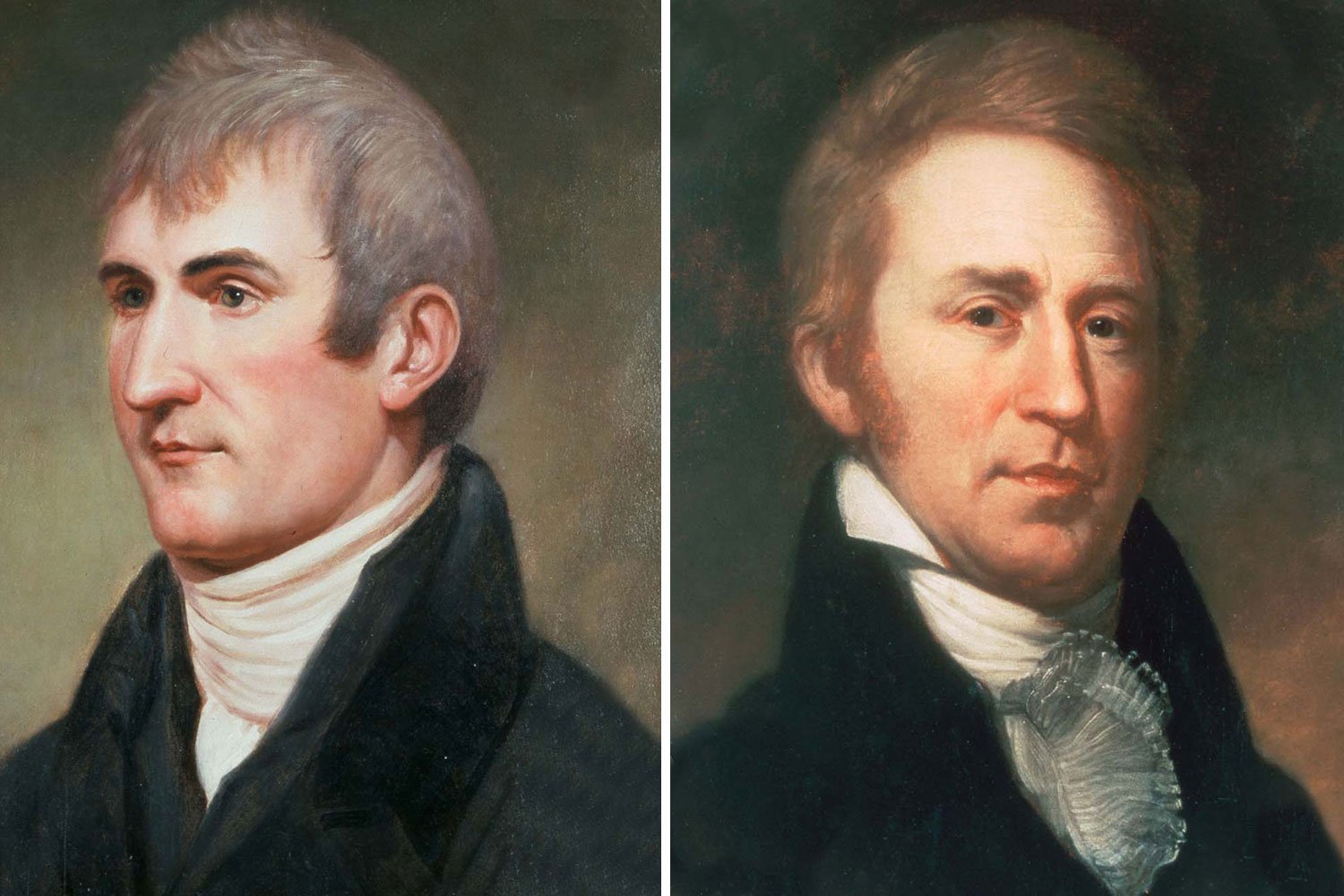

Lewis and Clark Expedition, Part 3: Leaders of the Corps of Discovery
In 1801, Meriwether Lewis was a Captain serving as the paymaster for the First Infantry Regiment of the United States Army. In March, he received a letter from Thomas Jefferson, the newly inaugurated President, asking Lewis to become his private secretary. Lewis, whose family was friends with the Jefferson clan, accepted at once, and thus began a close working relationship, one in which Jefferson became a father figure to Lewis and mentored his young subordinate on policy matters, including his dreams of western exploration and expansion.

Lewis and Clark Expedition, Part 2: Thomas Jefferson’s Western Vision
By the time they began to assemble the Corps of Discovery in the summer of 1803, Thomas Jefferson and Meriwether Lewis knew more than anyone else about the Louisiana Territory, that immense wilderness the country had recently purchased from France. Although Jefferson had never ventured more than fifty miles west from Monticello, he had dreamed of the trans-Mississippi and studied the region extensively over the previous two decades, even trying unsuccessfully to send exploratory expeditions on several occasions.

Lewis and Clark Expedition, Part 1: The Search for the Northwest Passage
The dream of finding an all water route across North America, the mythical Northwest Passage, had been imagined since the time of Christopher Columbus. Incredibly, three hundred years after the Admiral of the Ocean Seas completed his epic voyages, the vast interior of the continent was still essentially unknown to Europeans. This great uncertainty led to numerous theories about what lay beyond what men could see.
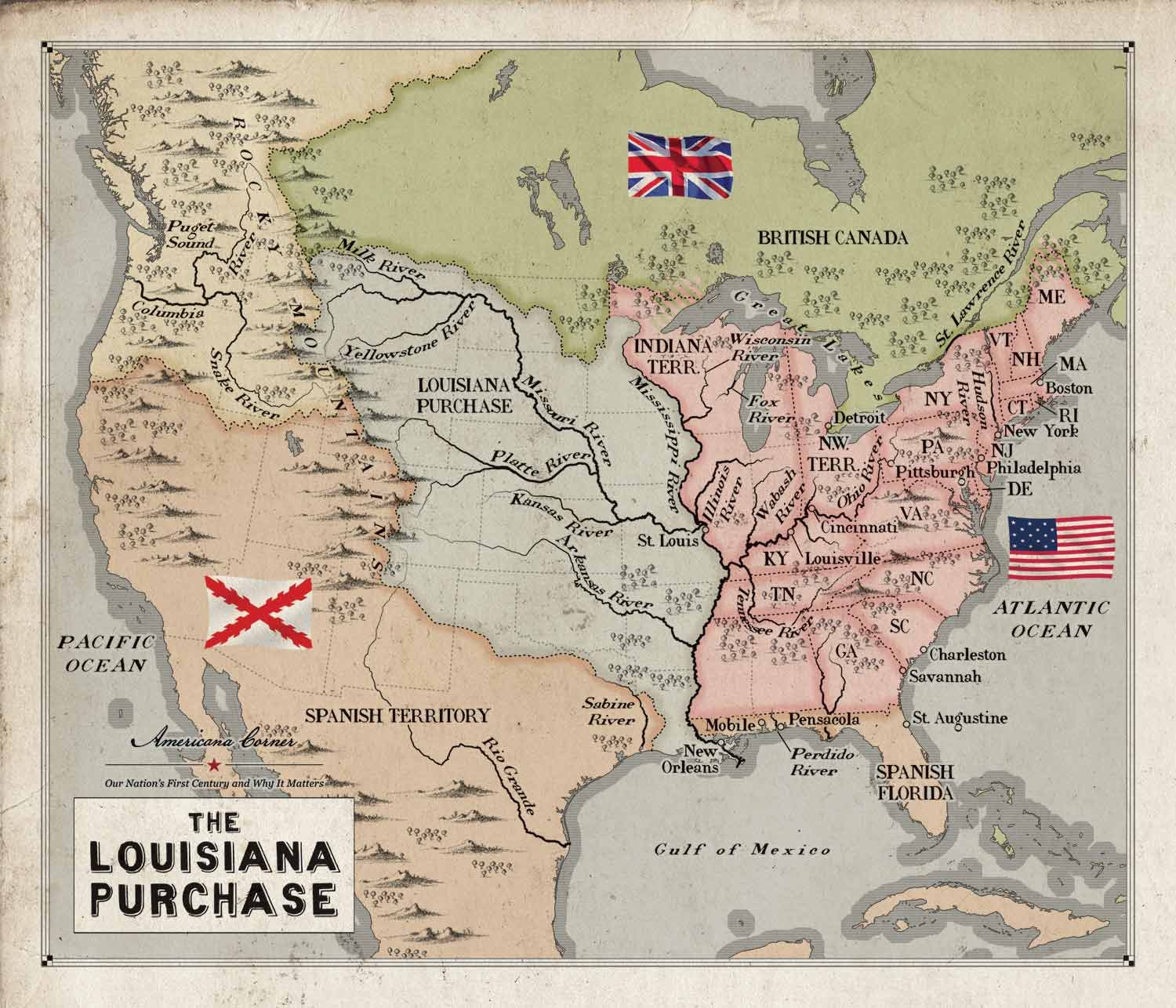
Louisiana Purchase, Part 4: “The Noblest Work of Our Lives”
The midnight deal Robert Livingston, United States Minister to France, struck with Francois Barbe-Marbois, Napoleon’s Finance Minister, on April 13, 1803, to purchase the Louisiana territory was one of the most impactful agreements in the history of the United States. It resulted from months of conversations Livingston had had with numerous French officials, creating a foundation for the details that would follow. But as important as this step was, there remained several hurdles to overcome.

Louisiana Purchase, Part 3: Napoleon’s Unexpected Gift
As a boy growing up in Virginia, Thomas Jefferson listened to his father tell captivating stories of the pristine wilderness beyond the Appalachian Mountains and dreamed of what opportunities lay in the uncharted lands of North America. As Jefferson grew to manhood, he became a proponent of national expansionism, recognizing that the future greatness of the country lay outside the original thirteen colonies.

Louisiana Purchase, Part 2: Western Settlement and the Mississippi River
The Treaty of Paris of 1783 which officially ended the American Revolution was generous to the United States, much more so than most had expected. Besides recognizing American independence, the provisions which Great Britain proposed greatly expanded the boundaries of the new nation, granting the United States all the land north of the Ohio River as far west as the Mississippi and as far north as British Canada. But like all gifts from adversaries, this one came with some issues that would simmer for decades.
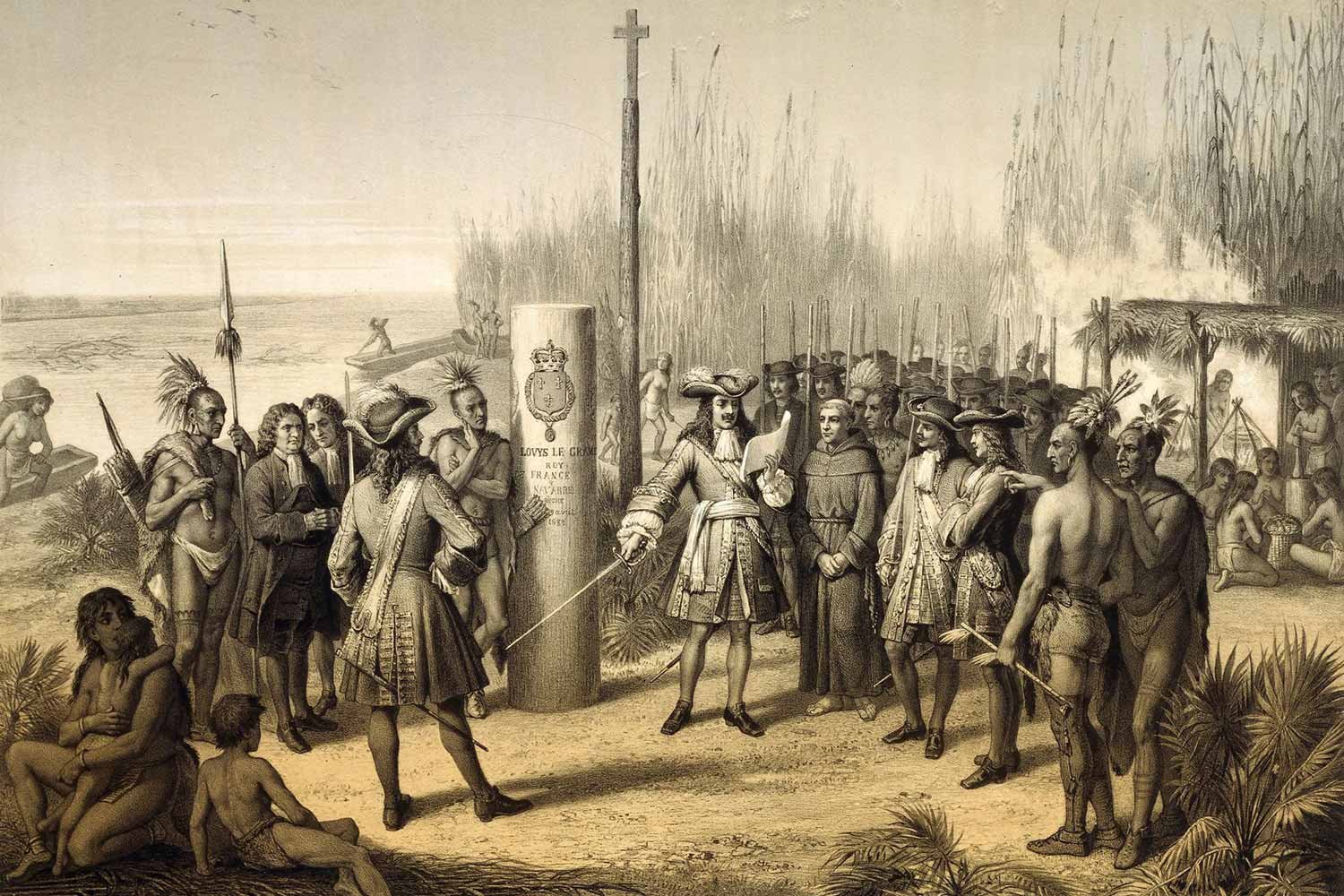

Louisiana Purchase, Part 1: The Early History of the Louisiana Territory
The Louisiana Purchase of 1803 was one of the truly watershed events in American history. The acquisition of this vast land placed the United States firmly on a path towards both the domination of North America and the status of an emerging world power.
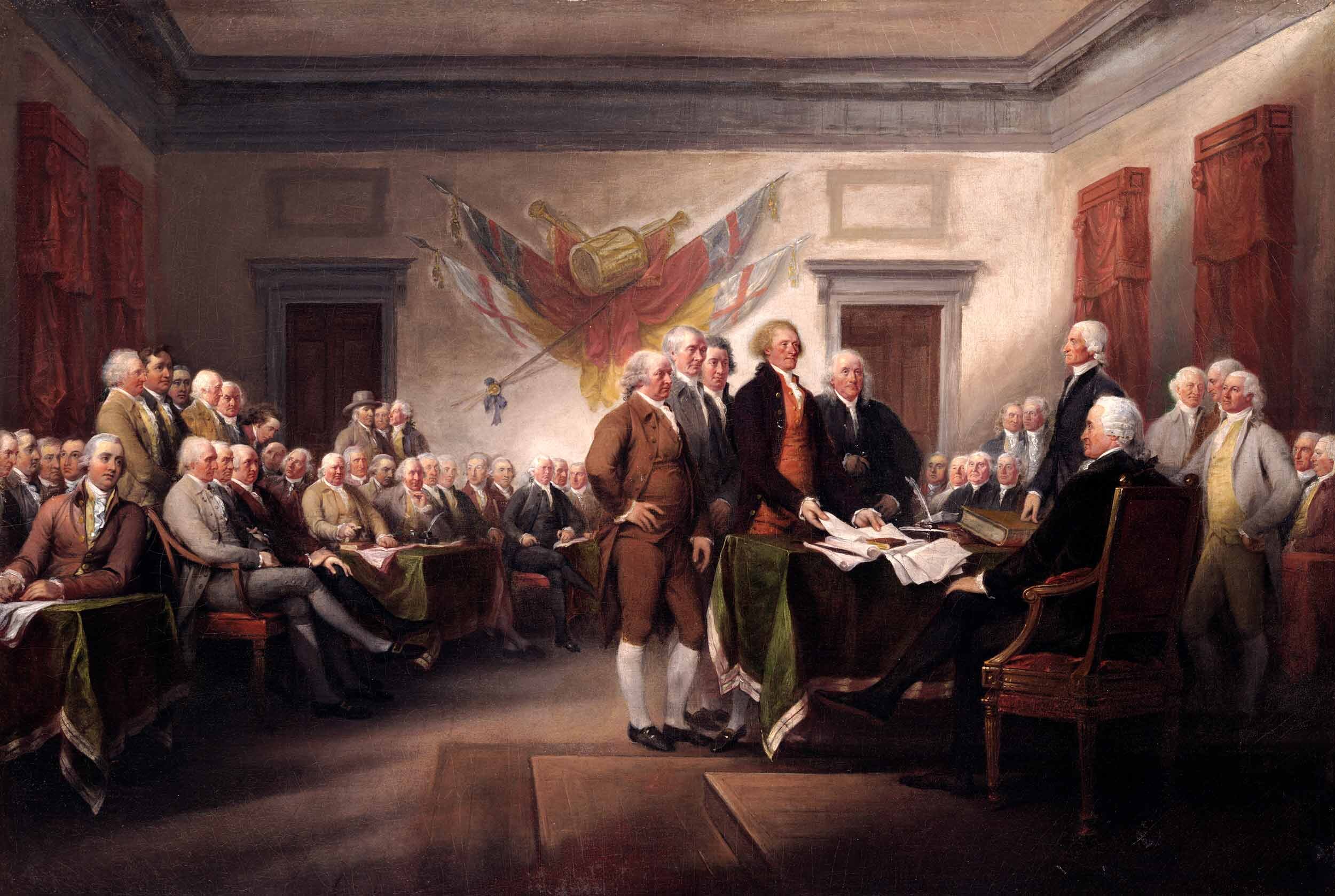

An Expression of the American Mind
On May 15, 1776, the fifth Virginia Convention meeting in Williamsburg passed a resolution calling on their delegates at the Second Continental Congress to declare a complete separation from Great Britain. Accordingly, on June 7, Richard Henry Lee rose and introduced into Congress what has come to be known as the Lee Resolution.
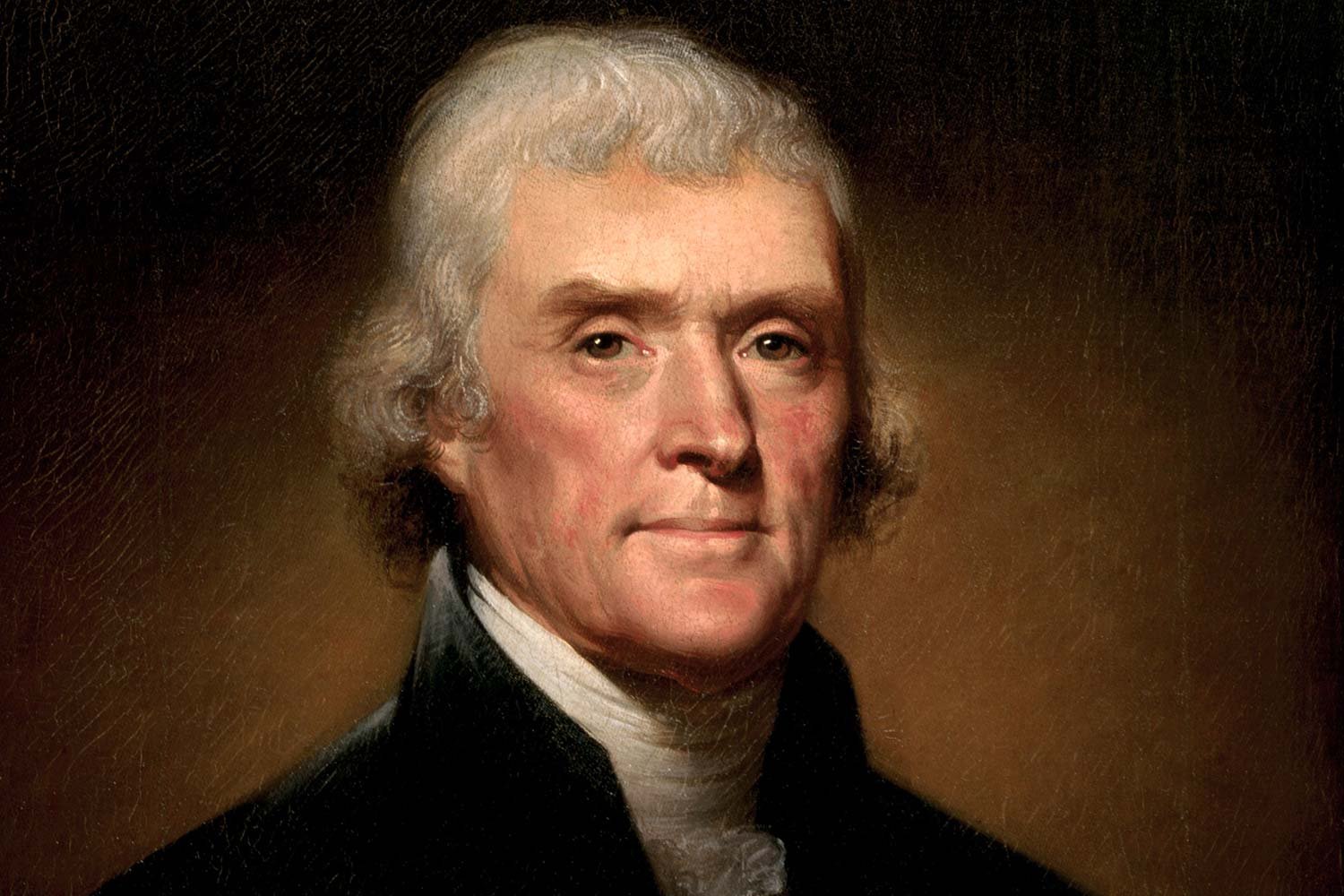

The Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions
In response to the Alien and Sedition Acts passed by the Federalist controlled Congress and signed by President John Adams in July 1798, Democratic-Republicans howled long and loud about the legislation that they viewed as an assault on both their party and the Constitution. They turned to their leader, Vice President Thomas Jefferson, to counter these Acts and, if possible, use them to their political advantage.

The Alien and Sedition Acts
The disrespect shown to the United States by France in the XYZ Affair in the spring of 1798 pushed the Federalists who controlled Congress to pass the Alien and Sedition Acts, a series of four laws, which President John Adams reluctantly signed into law in July. Posterity has viewed these measures harshly, but it is important to view them from the lens of 1798 and not modern times. At the time of their enactment, although many had reservations, the rationale behind them was not entirely groundless.
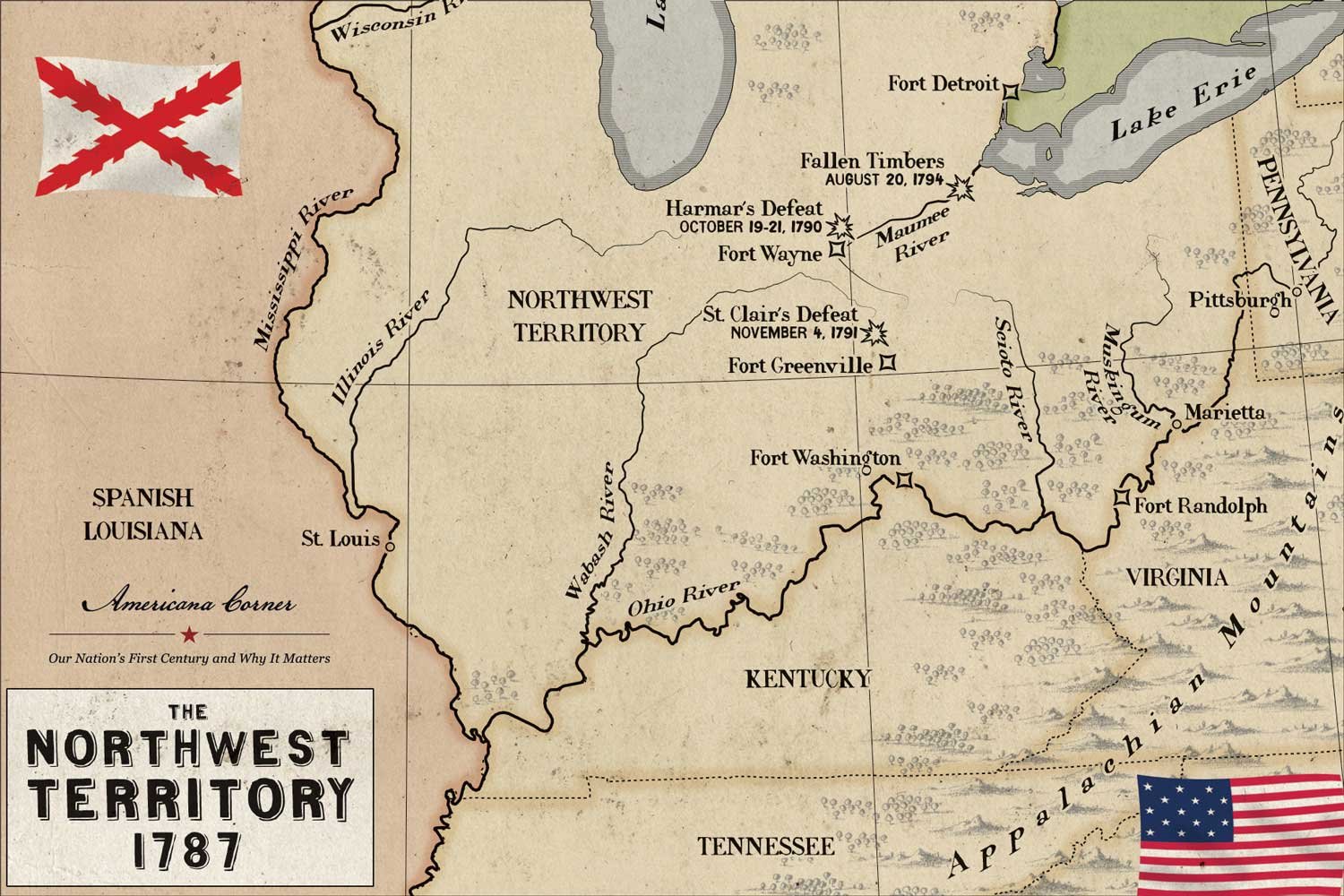
The Northwest Ordinance of 1787
The Northwest Ordinance was one of the United States most important founding documents, only less significant than the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution. The act, enacted by the Confederation Congress on July 13, 1787, created the Northwest Territory, officially known as the Territory of the United States North West of the River Ohio. This legislation created the country’s first organized incorporated territory and established a framework for further territorial expansions.




